DevContainers Setup in Visual Studio Code#
DevContainers provide a pre-configured development environment for PyRIT that ensures consistency across all contributors. This is the recommended setup for contributors using Visual Studio Code.
Note
Development Version: This setup uses the latest development code from the main branch, not a stable release. The notebooks in your cloned repository will match your code version.
Who Should Use DevContainers?#
✅ Use DevContainers if you:
Use Visual Studio Code as your editor. (Note that DevContainers can be used independently but our installation guide leverages VS Code since it’s seamless.)
Want a pre-configured development environment
Want consistency with other contributors
Prefer not to manage Python environments manually
Need all development tools and extensions pre-installed
❌ Consider local installation if you:
Use a different IDE or editor
Prefer full control over your development environment
Need to customize your setup beyond what DevContainers offer
Prerequisites#
Before starting, install:
Docker (Docker Desktop if you are using Windows)
Visual Studio Code
DevContainers Extension in VS Code
You can also follow the Installation section on Developing inside a Container for more details.
Setup Steps#
1. Clone the PyRIT Repository#
git clone https://github.com/Azure/PyRIT
cd PyRIT
2. Open in VS Code#
Open the PyRIT folder in Visual Studio Code:
code .
3. Reopen in Container#
Make sure Docker is running first, for example, by starting “Docker Desktop.”
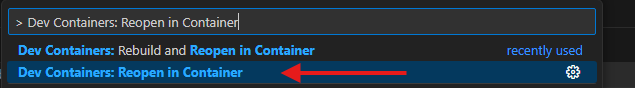
Press Ctrl + Shift + P (or Cmd + Shift + P on macOS) to open the VS Code Command Palette, then type and select:
Dev Containers: Reopen in Container
VS Code will:
Build the development container (this may take several minutes the first time)
Install all dependencies
Configure the development environment
Reopen VS Code inside the container
Tip
The first build takes longer as Docker downloads and configures everything. Subsequent opens will be much faster!
Working with Jupyter Notebooks#
Selecting a Kernel#
When working with Jupyter Notebooks (.ipynb files):
Open a notebook file in VS Code
Click the “Select Kernel” button in the top-right corner of the notebook
Choose “Python Environments…”
Select the
pyrit-devkernel
Alternatively, you can use the Command Palette:
Press
Ctrl + Shift + P(orCmd + Shift + Pon macOS)Type
>Notebook: Select Notebook KernelChoose “Python Environments…” >
pyrit-dev
This kernel will run all code examples in Python Notebooks.
Viewing Jupyter Variables#
To view variables populated by code examples:
Go to View > Output
Select Jupyter from the dropdown menu
Important
Note for Contributors: When constructing a pull request, notebooks should not be edited directly. Instead, edit the corresponding .py file. See Working with Notebooks for more details.
Populating Secrets#
After setting up your DevContainer, configure your API keys and secrets:
See Populating Secrets for detailed instructions.
Common DevContainer Operations#
Rebuild the Container#
If you need to rebuild the container (e.g., after dependency changes):
Press
Ctrl + Shift + P(orCmd + Shift + Pon macOS)Type and select:
Dev Containers: Rebuild Container
Reopen Locally#
To exit the container and return to your local environment:
Press
Ctrl + Shift + P(orCmd + Shift + Pon macOS)Type and select:
Dev Containers: Reopen Folder Locally
Troubleshooting#
Container Build Fails#
Problem: DevContainer fails to build
Solutions:
Ensure Docker is running
Check that you have sufficient disk space
Try rebuilding:
Dev Containers: Rebuild Container Without Cache
Extension Not Loading#
Problem: VS Code extensions don’t load in the container
Solution: Check the .devcontainer/devcontainer.json file to ensure extensions are listed. Rebuild the container if needed.
Performance Issues#
Problem: Container runs slowly
Solutions:
Allocate more resources to Docker in Docker Desktop settings
On Windows, ensure you’re using WSL 2 backend for better performance
Close unnecessary applications to free up system resources
