Building Smarter Apps: Integrating Phi-3 SLM with Linux App Service
In our ongoing series exploring the integration of various sidecar scenarios with Linux App Service, we delve into an exciting new domain—building AI applications. Following our previous discussion on leveraging Redis as a sidecar, we now turn our focus to using Small Language Models (SLMs) to enhance the capabilities of your web applications.
In this post, we will demonstrate how to deploy Phi-3, a powerful SLM, as a sidecar to your Linux App Service. SLMs offer numerous advantages for web applications, including:
- More Lightweight & Efficient: This makes them more suitable for situations where computational resources are limited or where real-time inference is required.
- More Accessible: SLMs lower the barrier to entry for people who want to experiment with language models. Anyone who has access to a laptop or mobile device can train and deploy an SLM, whereas training and deploying an LLM would likely require expensive cloud services or specialized hardware.
- Domain-Specific Adaptation: You can fine-tune SLMs to specific industry domains, such as legal, finance, or e-commerce, to improve performance and accuracy. This domain-specific adaptation allows the model to understand specialized terminology and context better, leading to more accurate results and insights. By tailoring SLMs to their specific use cases, organizations can unlock new opportunities for innovation and differentiation in their respective industries.
- More Secure: Since SLMs have smaller codebases and fewer potential surfaces for security breaches, they are also less vulnerable to malicious attacks.
- Better for the Environment: SLMs use less energy and memory than LLMs, which makes them more environmentally friendly and sustainable. They also have smaller footprints and faster inference times, which makes them more suitable for edge computing and real-time applications.
Setting Up the Application
For our sample application, we are creating a simple Node.js chat app. You can clone this repo if you would like to follow along.
This app will serve as the front end for interacting with the Phi-3 Small Language Model (SLM) running as a sidecar. You can find the code of the app here.
This is the main part of the code.
app.post("/api/generate", (req, res) => {
request.post('http://localhost:11434/api/generate', { json : {
"model": "phi3",
"prompt": req.body.prompt,
"stream": false,
"options": {
"num_keep": 5,
"num_predict": 150,
"seed": 42,
"top_k": 1,
"top_p": 0.9,
"tfs_z": 0.5,
"typical_p": 0.7,
"repeat_last_n": 33,
"temperature": 0.8,
"repeat_penalty": 1.2,
"presence_penalty": 1.5,
"frequency_penalty": 1.0,
"mirostat": 1,
"mirostat_tau": 0.8,
"mirostat_eta": 0.6,
"penalize_newline": true,
"stop": ["<*end*>"],
"num_thread": 8
}
}}
, (error, response, body) => {
if (error) {
console.error(error);
return;
}
res.json(body);
})
});
- This route handles POST requests to the /api/generate endpoint.
- It forwards the request to the Phi-3 SLM API running locally on port 11434.
- The request body includes the model configuration and prompt, along with various options for generating the response.
- The server sends the response from the SLM API back to the client.
Building your application container images
Prerequisites: Ensure you have Docker Desktop installed.
-
To get started, you’ll need to containerize your Node.js application. This article walks you through the process step by step.
Note: The Sidecar feature is currently enabled for custom-container scenarios for Linux App Service. We are working on enabling it for code scenarios as well. We will update the blog soon for the code-based web applications
The Dockerfile for this project is here.
Build the image and push it to your preferred container registry, such as Azure Container Registry, Docker Hub, or a private registry.
docker build -t <your-registry>/<your-image-name>:<tag> . docker push <your-registry>/<your-image-name>:<tag> -
Build the Phi-3 container image as well and push it to your container registry. You can use this Dockerfile.
For our Phi-3 images, we are also using a startup file
#!/usr/bin/env bash # Start Ollama in the background ollama serve & sleep 5 # Pull and run phi3 ollama pull phi3 # Restart ollama and run it in to foreground. pkill -f "ollama" ollama serveThis startup file performs the following actions:
- Starts the Ollama server in the background and waits for 5 seconds to ensure it is running.
- Pulls the Phi-3 model using Ollama.
- Restarts the Ollama server by killing the existing background process and then running it in the foreground to ensure the Phi-3 model is loaded and ready for use.
Deploying the Application to Linux App Service
-
Create a New Linux Web App in Azure
Create a new Linux Web App from the portal and choose the options for Container and Linux.
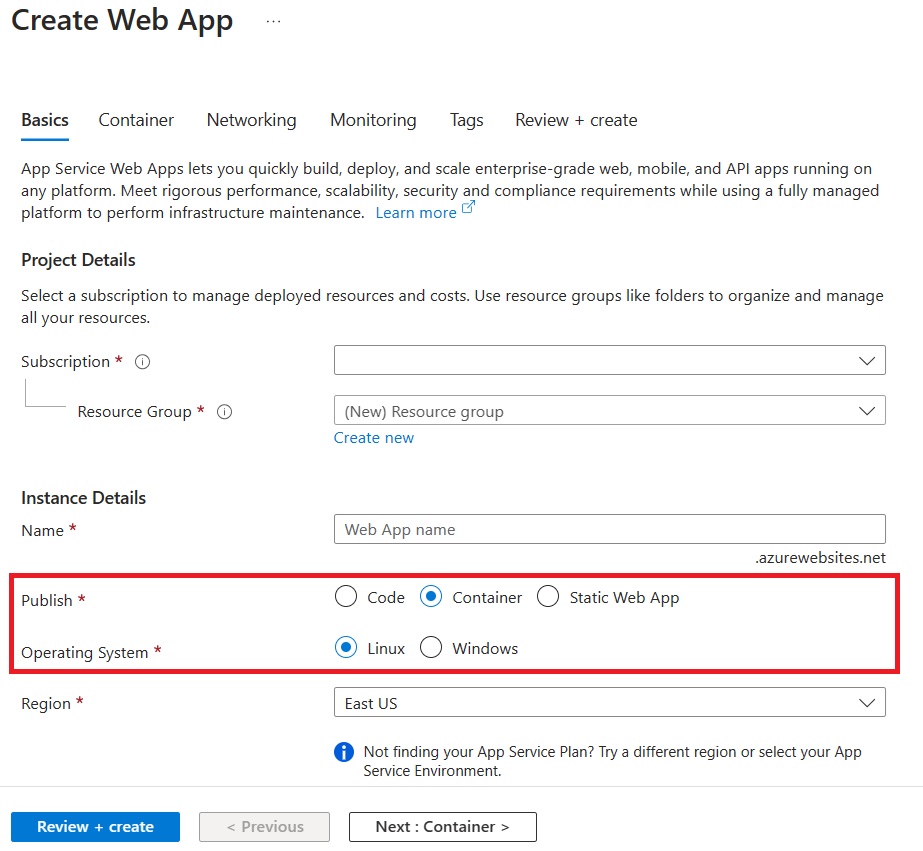
On the Container tab, make sure that Sidecar support is Enabled.
Specify the details of your application image.
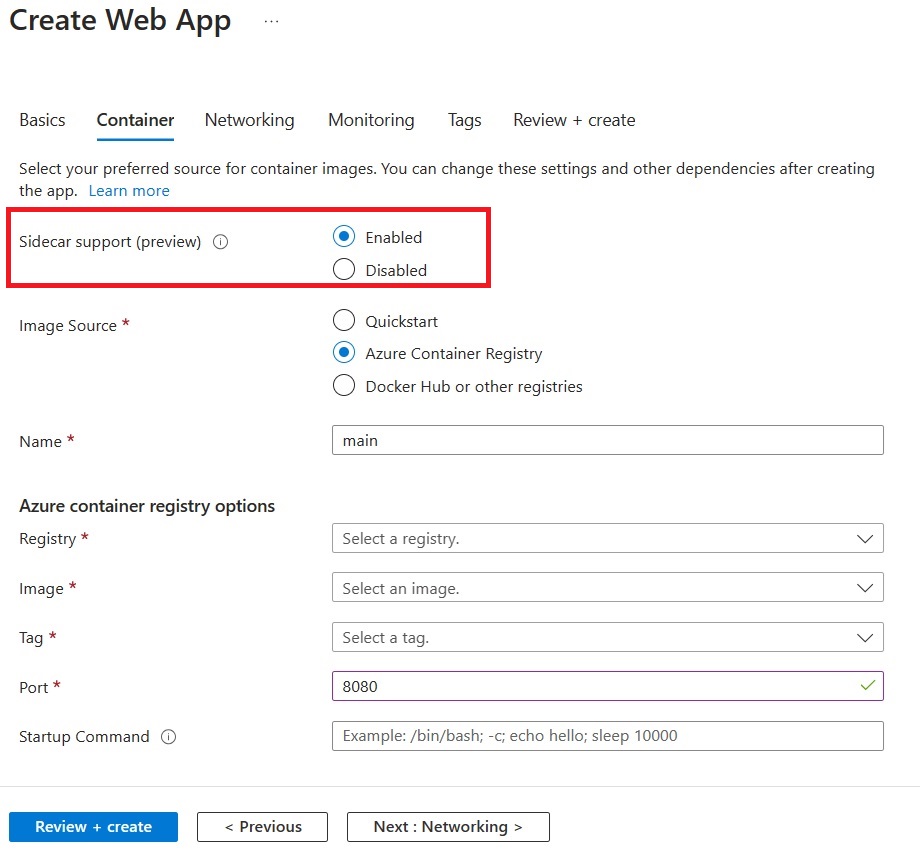
Note: We strongly recommend enabling Managed Identity for your Azure resources.
-
Add Phi-3 Sidecar
Go to the Deployment Center for your application and add a sidecar container.
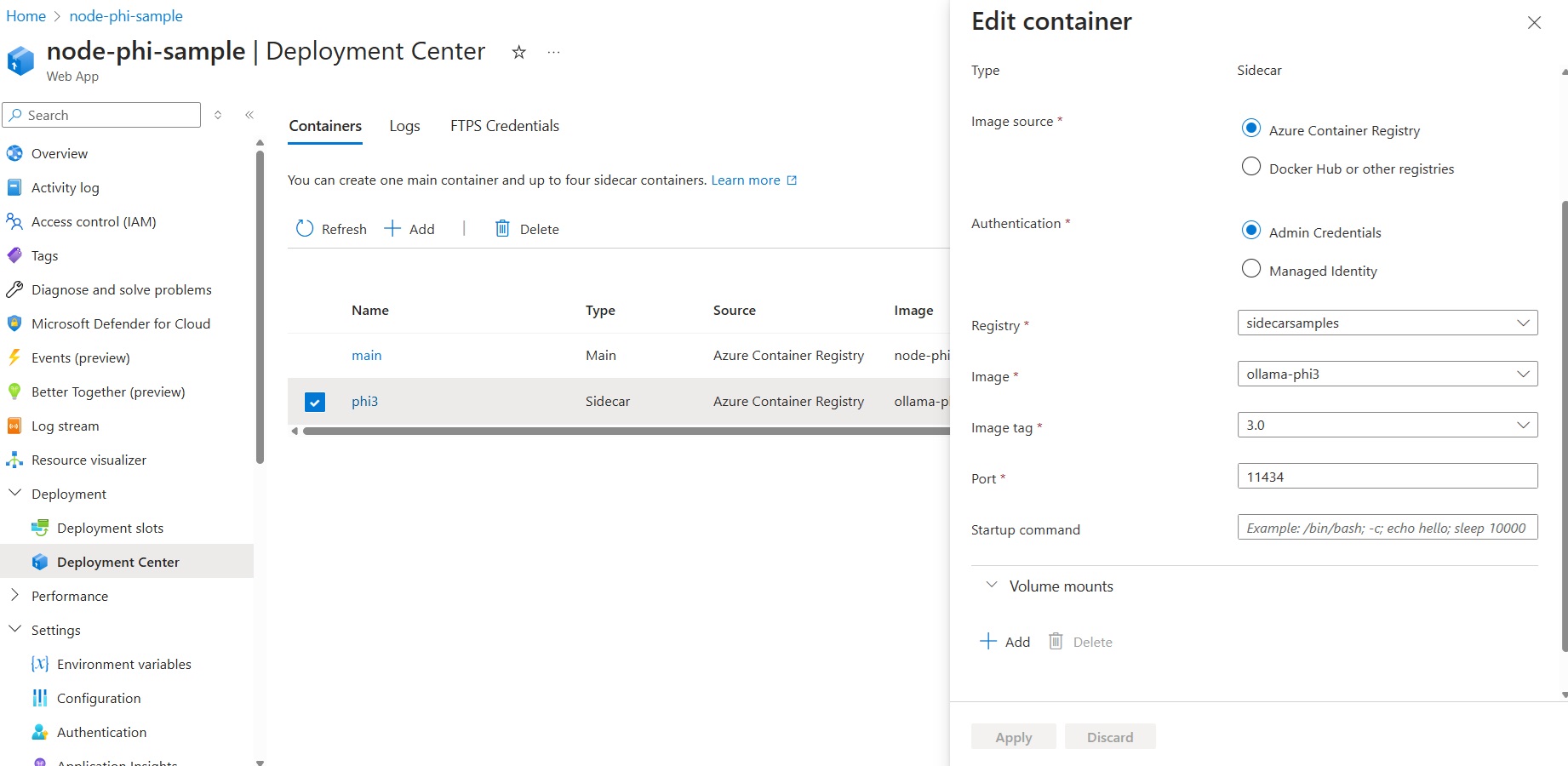
This document tells you how to add sidecars, step-by-step.
-
Verify the deployment
Once your deployment is complete, you can browse to your application URL and see the chat frontend.
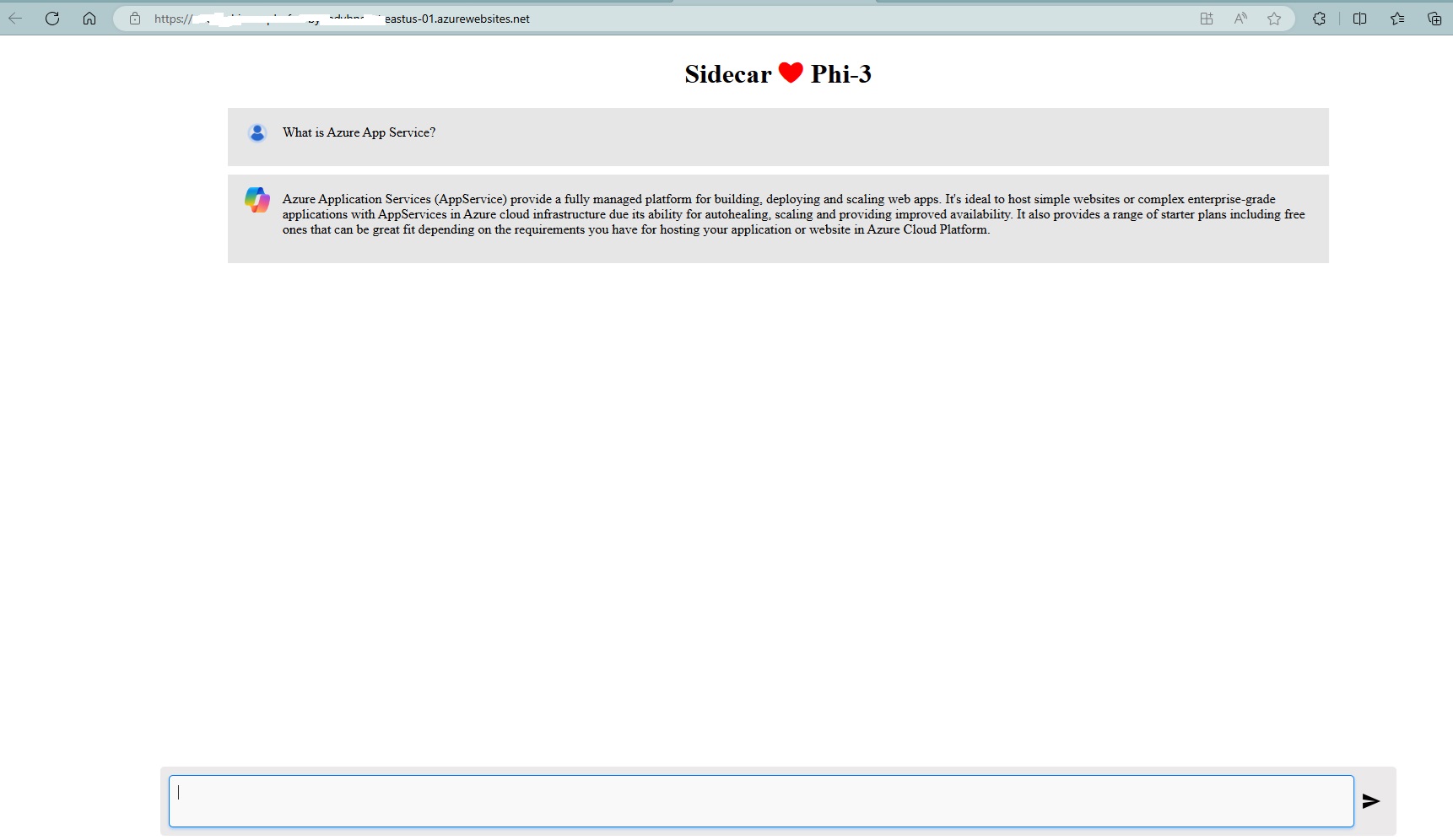
Note: Since we are deploying a language model, please be aware that the application might take a little longer to start up the first time. This delay is due to the initial setup and loading of the Phi-3 model, which ensures that it is ready to handle requests efficiently. Subsequent startups should be faster once the model is properly initialized.
Summary
In this blog post, we explored how to deploy Phi-3, a Small Language Model (SLM), as a sidecar on Linux App Service to add AI capabilities in your web applications. We discussed the benefits of using SLMs, such as being more lightweight, accessible, and secure, as well as their suitability for domain-specific adaptation and environmental sustainability. We also walked through the setup of a simple Node.js chat application that interacts with Phi-3, providing a practical example of how to integrate SLMs into your projects.
For more examples of Phi-3, feel free to explore this repository.
While we’ll continue to build and share more exciting sidecar scenarios, we can’t wait to see the amazing applications you create with these powerful features!
