Updates to App Service Azure Policies that monitor language versions
Azure Policy for App Service has the following built-in policies that ensure you are using the latest versions of certain languages that are available on the platform.
- App Service apps that use Java should use the latest ‘Java version’
- App Service apps that use Python should use the latest ‘Python version’
- App Service apps that use PHP should use the latest ‘PHP version’
- Function apps that use Java should use the latest ‘Java version’
- Function apps that use Python should use the latest ‘Python version’
Updates
We know that for certain customers, using the latest version of a language or runtime isn’t always possible. Additionally, with the variations and possible language versions available, we want to provide a way for our customers to have more flexibility when monitoring the compliance of languages used by their apps. For these reasons, the above policies have been modified. The following changes have been implemented and will be visible in the Azure portal in the next few weeks.
- The policies no longer have a hard-coded value for the language version they’re monitoring. Instead, the user must specify a version that aligns with their requirements when assigning these policies.
- When assigning these policies, users will be prompted to specify a language version.
- The policies have been renamed to align with this updated scope. Below are the new names.
- App Service apps that use Java should use a specified ‘Java version’
- App Service apps that use Python should use a specified ‘Python version’
- App Service apps that use PHP should use a specified ‘PHP version’
- Function apps that use Java should use a specified ‘Java version’
- Function apps that use Python should use a specified ‘Python version’
- The policies have been removed from the Azure Security Baseline and Microsoft Defender for Cloud initiatives.
- The policies can still be assigned and even added to a Microsoft Defender for Cloud initiative, however they won’t be automatically assigned as they previously were.
- Equivalent policies have been created to monitor compliance for slots. These must be assigned in addition to the policies that monitor the main site in order to ensure monitoring is in place for all App Service resources.
- App Service app slots that use Python should use a specified ‘Python version’
- Function app slots that use Python should use a specified ‘Python version’
- App Service app slots that use PHP should use a specified ‘PHP version’
- App Service app slots that use Java should use a specified ‘Java version’
- Function app slots that use Java should use a specified ‘Java version’
There are also a couple limitations to be aware of when using these policies.
- They’re scoped to apps on Linux App Service only.
- If you require monitoring for Windows apps, you can use the existing policies as a reference to create Windows specific custom policies. For more information on building and assigning custom policies, see Tutorial: Create a custom policy definition.
- These policies use text based matching on a “free-text” field to monitor compliance. Ensure you have proper controls in place to prevent unexpected changes to language versions.
Required actions
These policy updates will have no impact on existing policy assignments. If you have the old version of these policies assigned, they will continue to function without interruption. In order to use the new versions of these policies, you must create new policy assignments. We encourage you to take this action as soon as possible as the old versions of these policies are prone to false negatives.
How to use the new policies
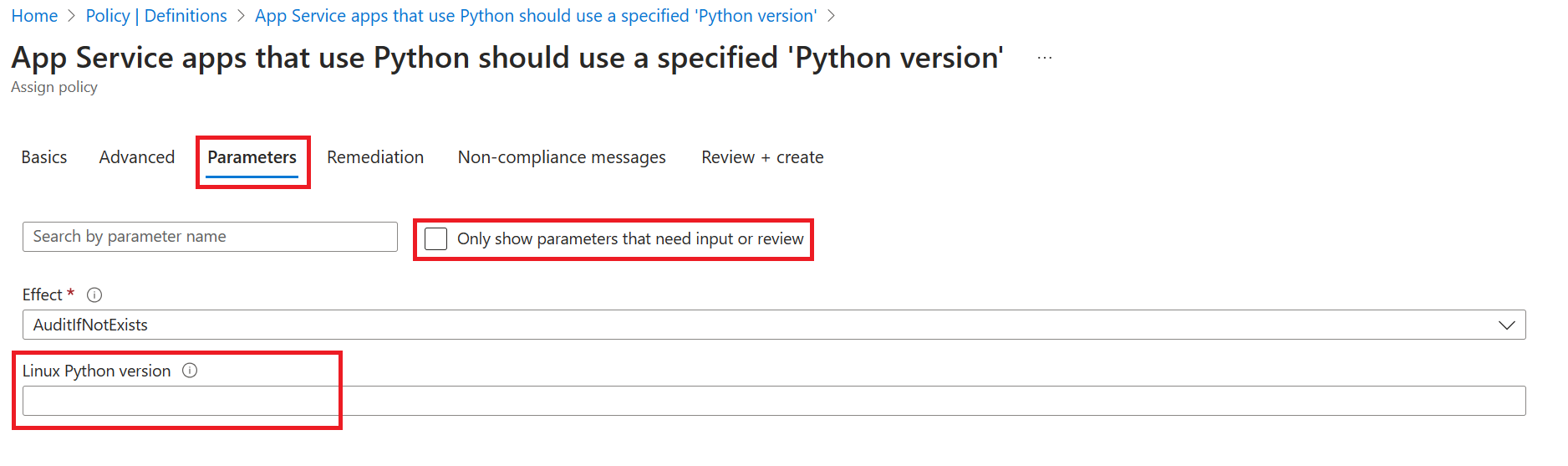
The new policies can be assigned in the Azure portal. For more information on how to assign policies, see Assign a policy to a resource group.
When assigning these policies in the Azure portal, you won’t automatically be prompted to specify a language version. You must go to the Parameters tab and uncheck the box “Only show parameters that need input or review” in order to see the language version parameter. This is a required parameter that defaults to an empty string so if you don’t specify a value, the policy will always evaluate to non-compliant.