Configuring Network Services for an Avere Cluster
When setting up an Avere OS cluster, you will need to plan for the items described here.
Some network configuration needs to be handled at the network adminstrator level, and it is not practical for any Avere components to take the place of a network switch or router. However, Avere has incorporated support for certain networking features that are commonly used by storage administrators into Avere OS.
Additional information is included in the FXT Cluster Creation Guide. Be sure to read that document before attempting to configure the network infrastructure.
Subnetworks and IP Address Ranges
You can configure multiple VLANs and set reserved IP address ranges for different types of traffic. Optionally, you can organize each into separate VLANs.
There are three main categories.
Management Network
- Management IP Address Range (optional)
A fixed range of addresses used for node management traffic. Specify one or more address ranges on the Cluster > Administrative Network settings page.
The management IP range is used to provide a fixed management address to each node in the cluster. (The address range should include at least as many addresses as there are cluster nodes.) This is an optional step, but is recommended as a best practice.
- Management IP Address
A static IP address that is used to access the Avere Control Panel. This address is always assigned to the primary cluster node; if a primary (leader) node becomes unavailable, this IP address will move to the FXT node that becomes the new primary.
Configure the management IP address on the Cluster > Administrative Network settings page.
- Management Network Ports (optional)
- Optionally, you can configure the onboard 1GbE ports of your cluster’s FXT nodes as a separate network for management traffic. Read Separate Management Network on the Cluster > Administrative Network settings page description to learn more.
Cluster and Core Filer Network
- Cluster IP Address Range
- A fixed range of IP addresses used for communication between cluster nodes. Configure cluster IPs on the Cluster > Cluster Networks settings page.
- Core Filer IP Addresses
- A fixed range of IP addresses used for cluster to core filer communication
Port Settings
Appendix D: Port Configuration lists the ports that should be accessible to the Avere cluster in a firewalled environment.
- Link Aggregation
- The Ethernet interfaces on the FXT nodes can be grouped to create failover redundancy with either static or dynamic link aggregation protocols.
- Port Groups
An advanced feature allows administrators to assign specific IP address ranges to a custom group of network interfaces. The configuration is complicated and there might be simpler methods available; contact Avere Global Services to learn more.
Note that port groups are supported only on clusters that use the same FXT hardware model for all nodes. Mixed-model clusters cannot use port groups.
Network Infrastructure
- DNS Settings
- Configure DNS server and domain information on the Cluster > Administrative Network page. Read Configuring DNS for the Avere cluster to learn more about configuring DNS for your cluster.
- Time Settings
- To ensure consistent timestamps in your cluster, NTP servers are required. Time settings are configured on the Cluster > Administrative Network page.
Security and Encryption
Avere OS can be used with a variety of protocols to encrypt data and to provide client authentication and authorization.
Kerberos
Kerberos can be used for NAS core filer authentication. Read Setting Up Kerberos Authentication to learn more.
LDAP and AD
Configure user authentication services on the Cluster > Directory Services page; you can use LDAP, AD, NIS, or another method to populate user and group tables.
Different settings are included for SMB and NFS access.
Cloud Core Filer Access and Data Encryption
There are several options for protecting access to data stored in the cloud.
You can use a KMIP-based system to encrypt the content of a cloud data store. Configuring KMIP for an Avere cluster explains the steps required and gives links to the relevant configuration steps on the Cluster > Cloud Credentials and Cluster > KMIP Servers pages.
Also, you can set the default protocol to HTTPS for core filer communication when you create a cloud core filer, or on the Core Filer > Core Filer Details page.
Working with VLANs
You can use virtual local area networks (VLANs) to connect components of the Avere cluster (core filers, vservers, and nodes).
Note that all VLANs must be accessible by all nodes in the cluster. However, you can specify particular VLANs to be used for particular vservers.
Note
If advanced networking is disabled, VLAN configuration is unavailable. Read About “Advanced Networking” for more information. Clusters created with Avere OS 4.5 or later have advanced networking features by default.
When a cluster is created, a default (untagged) VLAN is automatically created. You cannot remove the default VLAN, but you can create additional VLANs with customized settings.
If the IP address range or VLAN number for any network interface is changed, the interface is temporarily unavailable while the changes are committed.
Static Routes
Avere OS allows you to add manual routing entries for routers that service the cluster.
VLAN Roles
You can specify one or more roles for each of your cluster’s VLANs. A VLAN’s role controls which lists it appears in when selecting VLANs in the Avere Control Panel.
If you use reserved IP address ranges for various functions, you might want to associate a reserved address range with a certain type of VLAN to avoid accidentally using addresses inappropriately. In general, though, there is no reason for a VLAN to not have all roles.
Set or change a VLAN’s roles in the Cluster > VLAN settings page.
Currently available roles are:
Client Role VLANs
VLANs with the role Client are used by vservers to serve client requests.
They appear in the VLAN selector when creating a vserver (from the VServer > Manage VServers page) or when editing a vserver’s IP range on the VServer > Client Facing Network settings page.
Cluster Role VLANs
VLANs with the role Cluster are used to communicate among the nodes in the cluster, and also between the cluster and the core filers.
These VLANs can be selected when creating or modifying IP address ranges for a cluster network, on the Cluster > Cluster Networks settings page.
Optionally, you can reserve a range of IP addresses that are available exclusively for the use of cluster role VLANs.
Important
Before selecting a VLAN for cluster interfaces, make sure that all components of both the current cluster network and the new cluster network are functioning correctly. Check that cluster traffic is being transmitted across the existing cluster network and all interfaces. If any component of the original or new cluster network is unavailable when the configuration changes, it is possible for the cluster to enter a bad state, causing file service disruptions or other failures.
When you modify or enable a VLAN for cluster interfaces, the change propagates through the existing cluster network. Services and internal processes restart on each node in the cluster in order to use the new VLAN.
A cluster VLAN is used for communication between the cluster and the core filers as well as among nodes. Cluster VLANs must use the default gateway assigned to the cluster.
Core Filer Access Role VLANs
VLANs with the role Core filer access are used to communicate between cluster nodes and core filers. (Cluster VLANs also can be used for core filer access.)
These VLANs can be selected when creating or modifying IP address ranges for a cluster network, on the Cluster > Cluster Networks settings page.
Management Role VLANs
Management role VLANs are used by storage administrators to access the FXT nodes in the cluster. Optionally, you can reserve a range of administrative IP addresses that are available exclusively for the use of management role VLANs.
Only VLANs with the role Management can be selected in the Management VLAN list on the Cluster > Administrative Network settings page.
You can reserve a range of IP addresses for a management VLAN to use for node management. Refer to Node Management Addresses for more information.
Configuring DNS for the Avere cluster
This document explains the basics for setting up a DNS system for your Avere OS cluster.
If your system is accessed by NFS clients only, using DNS is recommended but not required (it is possible to specify all network addresses by using numeric IP addresses). If your system supports SMB (CIFS) access, DNS is required, because you must specify a DNS domain for the Active Directory server.
DNS also is required if you want to use Kerberos authentication.
Load Balancing
To distribute the overall load, configure your DNS domain to use round-robin load distribution for client-facing IP addresses.
Configuration Details
For optimal performance, configure client-facing cluster addresses as shown in the following diagram.
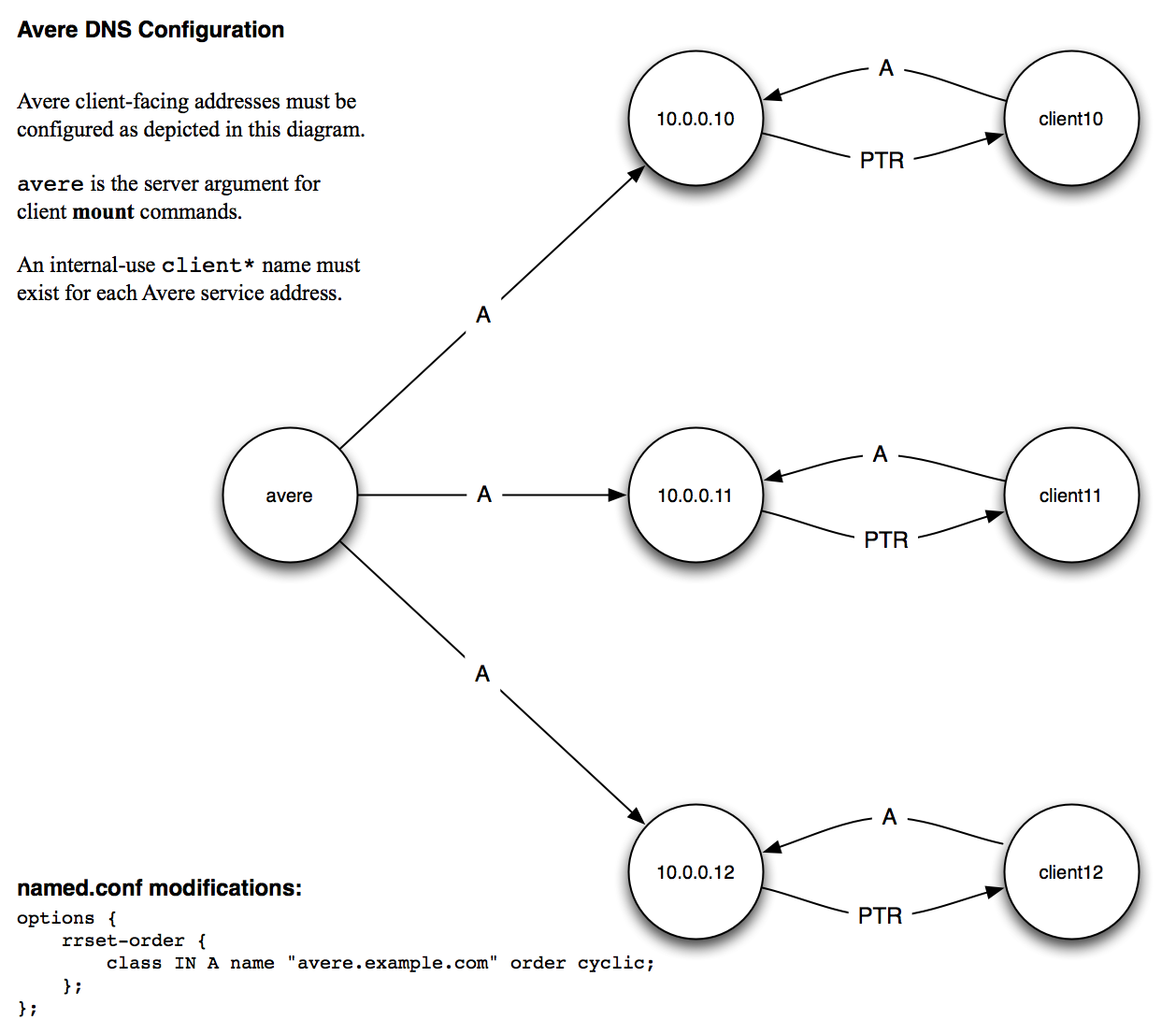
The following nsupdate commands provide an example of configuring DNS correctly:
update add avere.example.com. 86400 A 10.0.0.10
update add avere.example.com. 86400 A 10.0.0.11
update add avere.example.com. 86400 A 10.0.0.12
update add client10.example.com. 86400 A 10.0.0.10
update add client11.example.com. 86400 A 10.0.0.11
update add client12.example.com. 86400 A 10.0.0.12
update add 10.0.0.10.in-addr.arpa. 86400 PTR client10.example.com
update add 11.0.0.10.in-addr.arpa. 86400 PTR client11.example.com
update add 12.0.0.10.in-addr.arpa. 86400 PTR client12.example.com
DNS Settings
DNS parameters are set in the Cluster > Administrative Network settings page. Settings on that page include:
- DNS server address
- DNS domain name
- DNS search domains
Read DNS Settings for more details about using this page.
