Dive in to learn more about how our example application works at a technical level.
What we cover:
- A high-level architecture overview
- A description of API calls made by the front-end app
- An overview of the APIs offered by the middleware service
- A walkthrough of the back-end service’s APIs and integration with other Azure services
Introduction
In the previous blog post, we gave you a high-level overview of our example AI-based content generation app, covering its user experience and how it integrated various services. Now we’d like to dive a little deeper into the technical side, explaining the app's architecture, key components, and code snippets and offering an overview of the app’s data flow.
Today’s post breaks down how the front-end, middleware, and back-end services work together. We also discuss how the app uses Azure services, like Azure API Management, Azure Key Vault, Azure Cosmos DB, Azure Blob Storage, and Azure OpenAI Service, and how managed identity is used to securely connect these components.
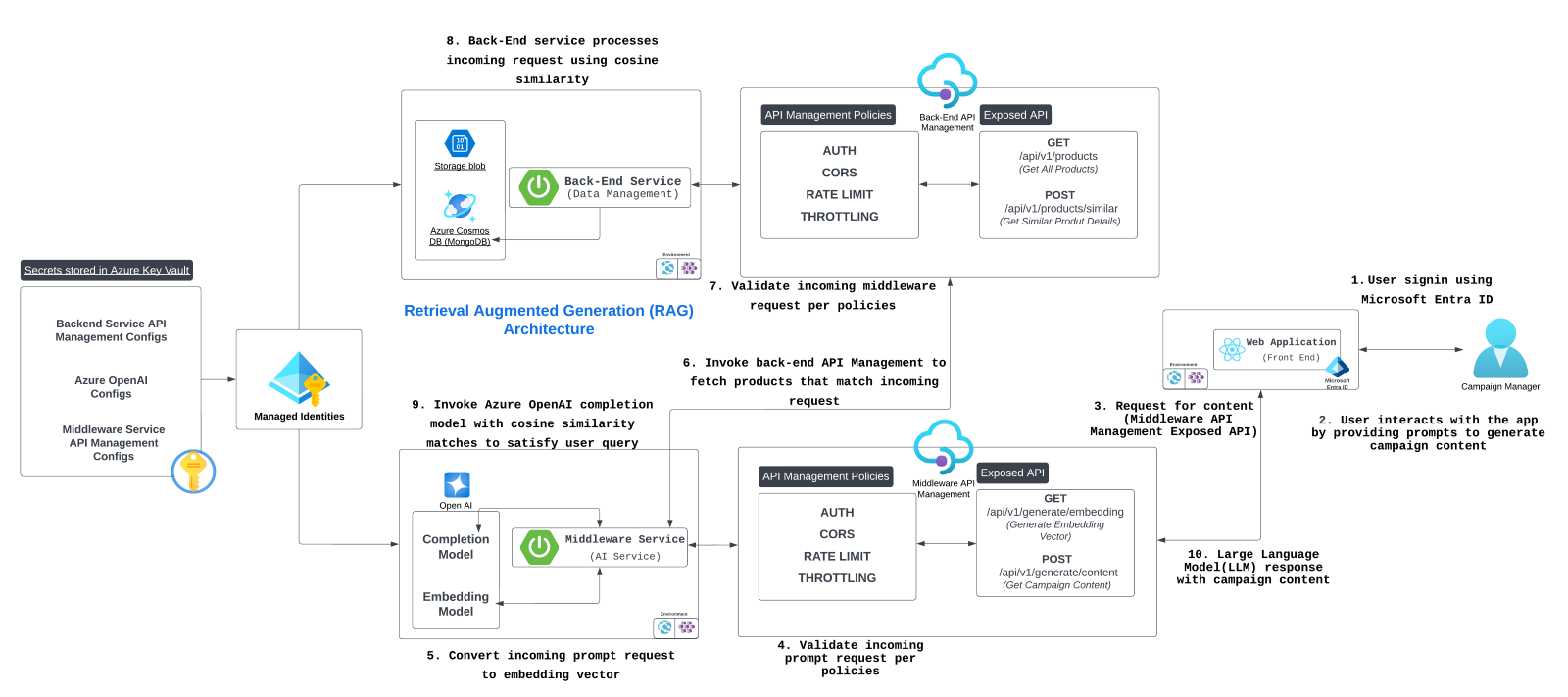
1. High-level architecture
The application is composed of three core services:
-
Front-end app (ReactJS based). A chat-based UI where users submit queries and receive AI-generated content
-
Middleware service (Java Spring Boot based). Responsible for content generation and handling product similarity searches
-
Back-end service (Java Spring Boot based). Handles customer and product data and computes product similarity using vectors
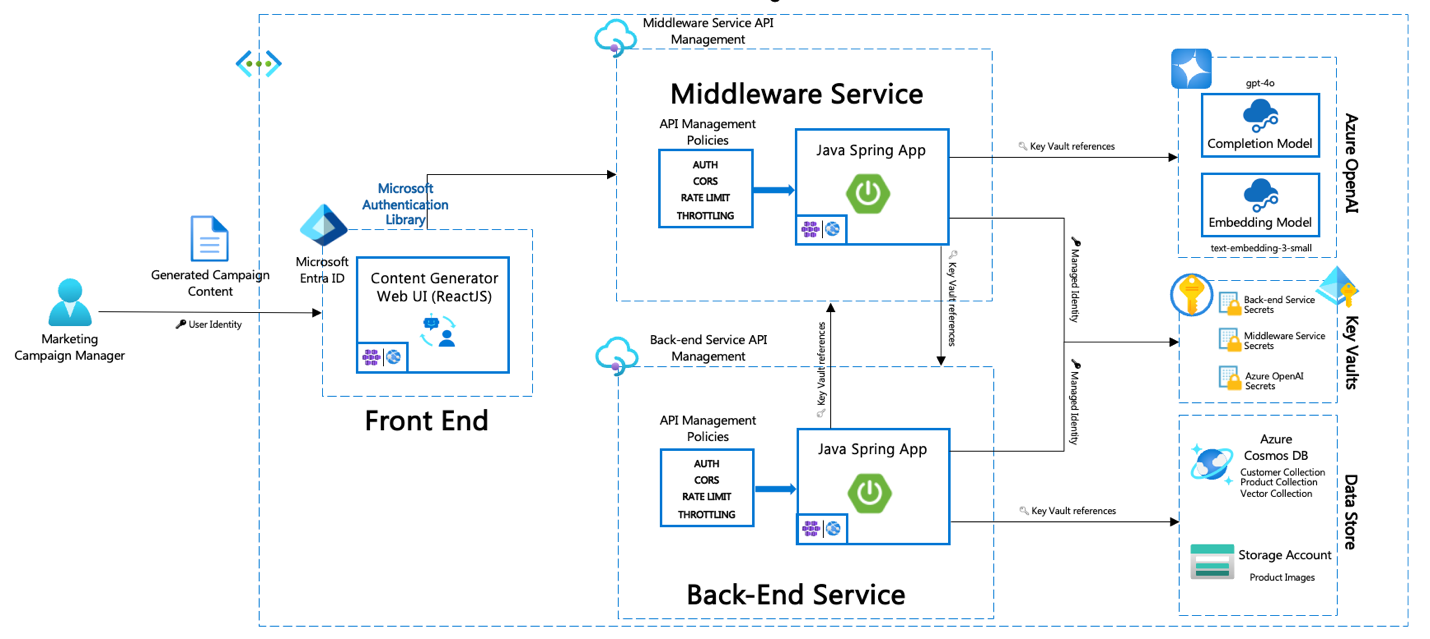
Architecture diagram
The architecture diagram shows the interaction between:
Front end -> Middleware Azure API Management endpoints -> Middleware service -> Back-end API Management endpoints -> Back end (Spring Boot).
How middleware and back-end services connect to Azure Key Vault, Azure Cosmos DB, Azure Blob Storage, and Azure OpenAI.
2. Front-end app
The front end acts as the interface between the user and the application. It allows the user to sign in, enter queries, and receive generated content.
Key components:
-
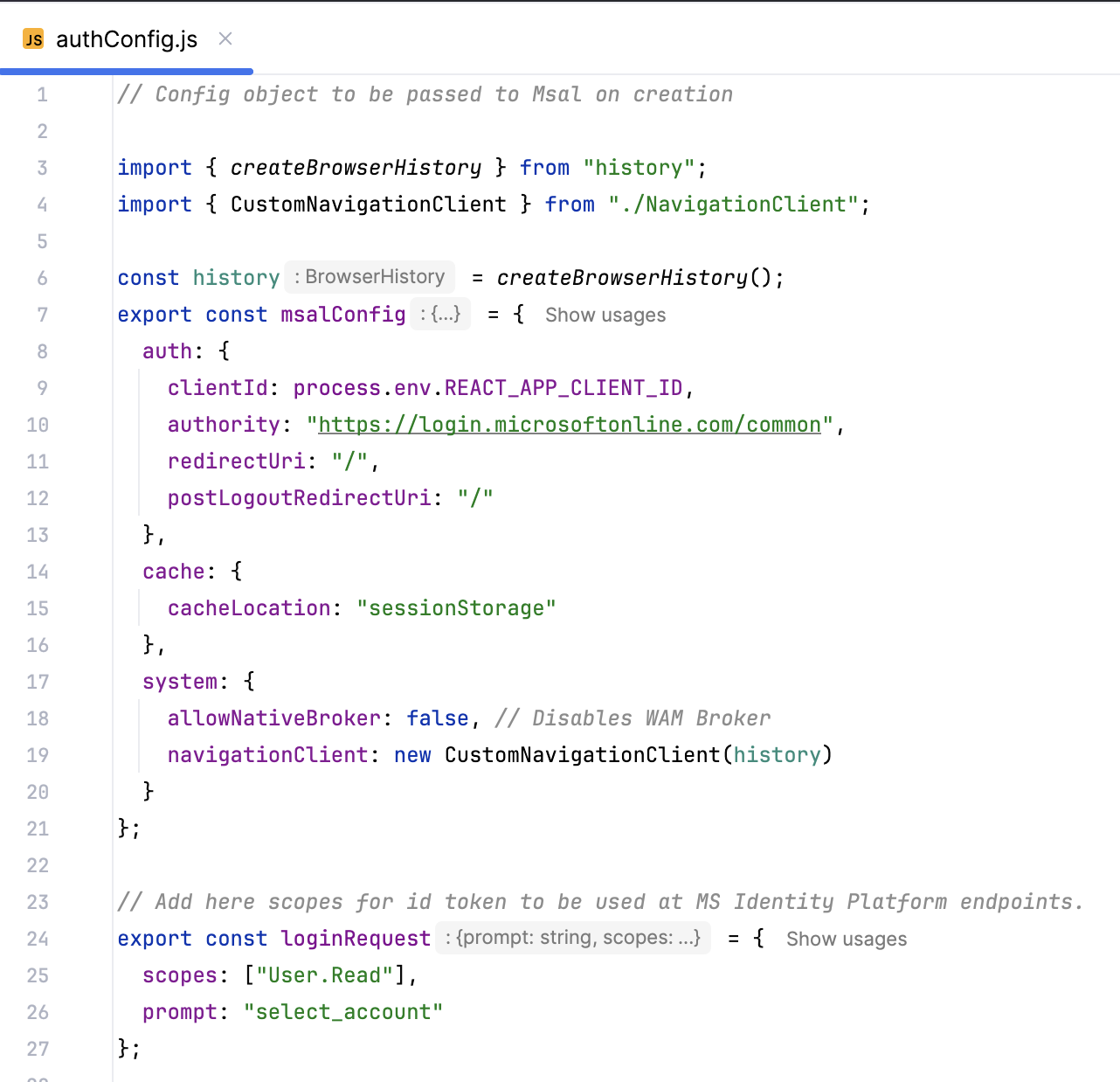
Sign-in and user identity management. The front end uses identity management to authenticate users before they access the main chat functionality.
- Code snippet: User authentication logic uses the Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL). (@azure/msal-browser)
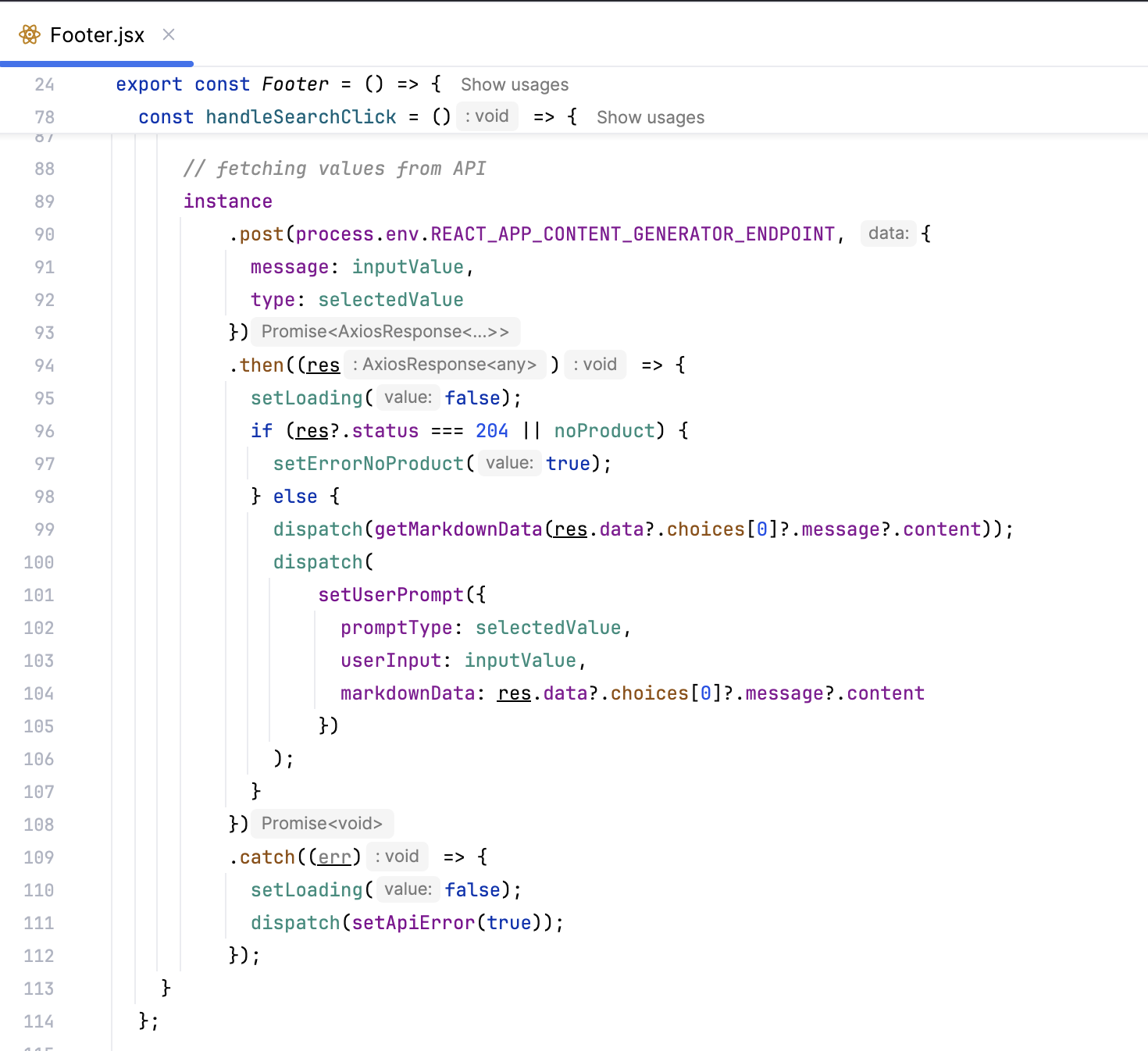
- Chat interface. After authentication, the user can interact with the chat interface. On form submission, the query is sent to the Middleware API through an API Management endpoint.
3. Middleware service
The middleware service is the central hub for content generation and managing product similarity searches. It connects to Azure OpenAI for content generation and interfaces with the back end to retrieve product vectors.
Core APIs:
- Generate content API. This API receives the user’s query, generates an embedding vector, and calls Azure OpenAI to generate relevant content.

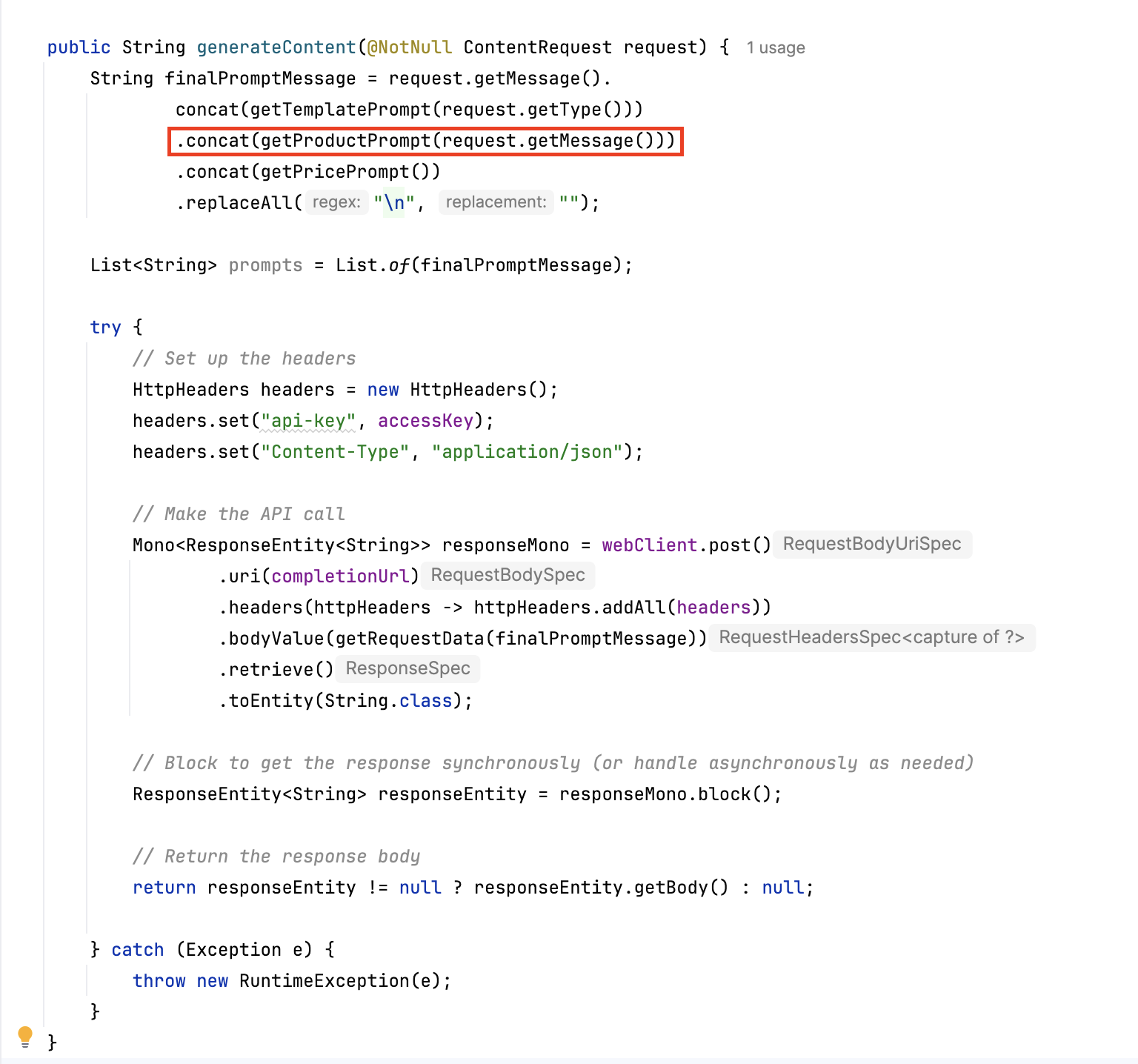
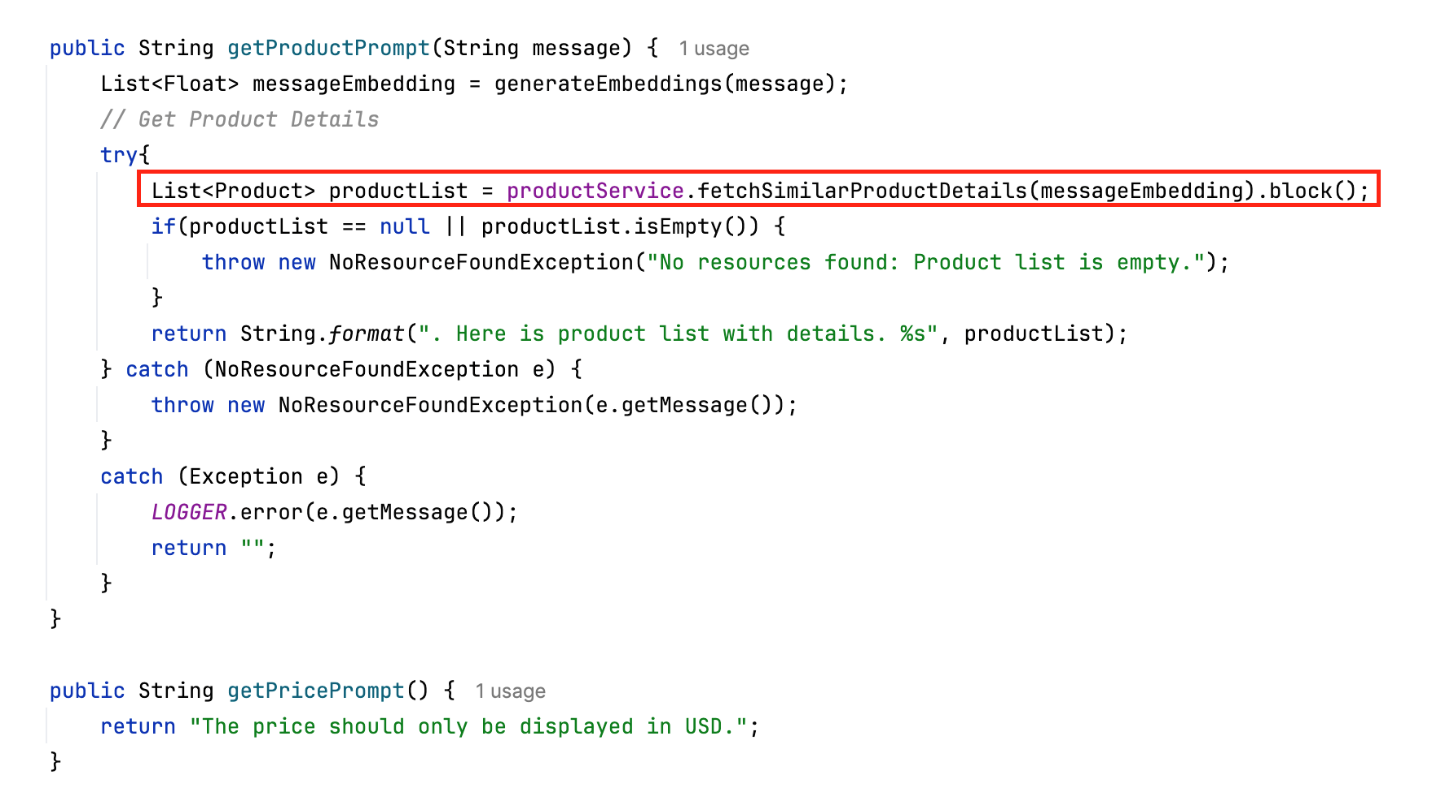
- Generate embedding vector API. Uses OpenAI's embedding model to transform the user query into an embedding vector that the back-end service can use for similarity matching.
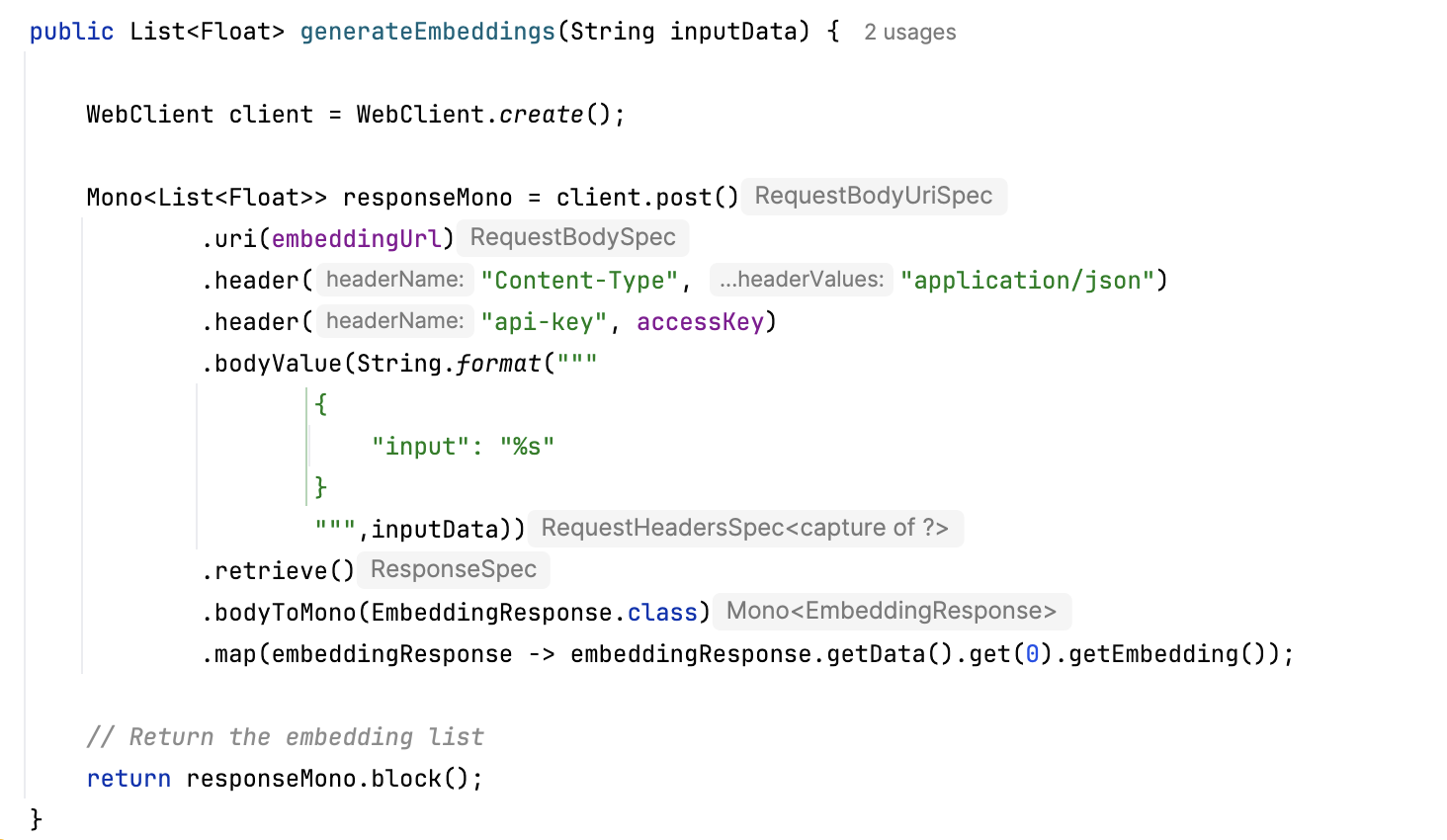
- OpenAI integration. The middleware connects to OpenAI's GPT-4o completion model for content generation and text embedding model for vector creation. Credentials and API keys are retrieved securely from Azure Key Vault using a managed identity.

4. Back-end service
The back-end service handles customer and product data and uses the product vector API to find similar products based on embedding vectors sent from the middleware.
Core APIs:
- Customer API. Manages customer data and provides endpoints to retrieve and update customer information.
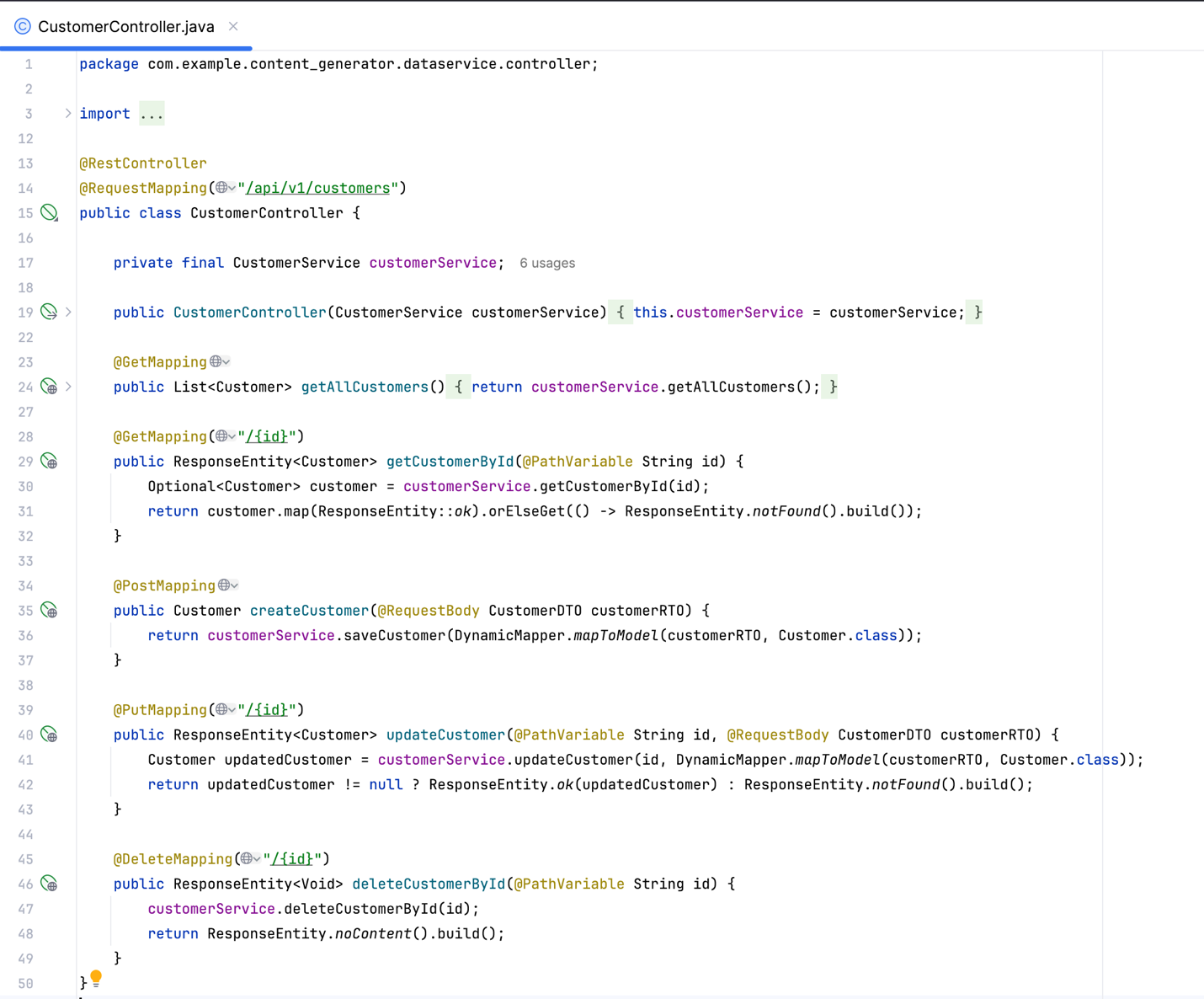
- Product vector API. Retrieves a list of similar products based on the embedding vector generated by the middleware.
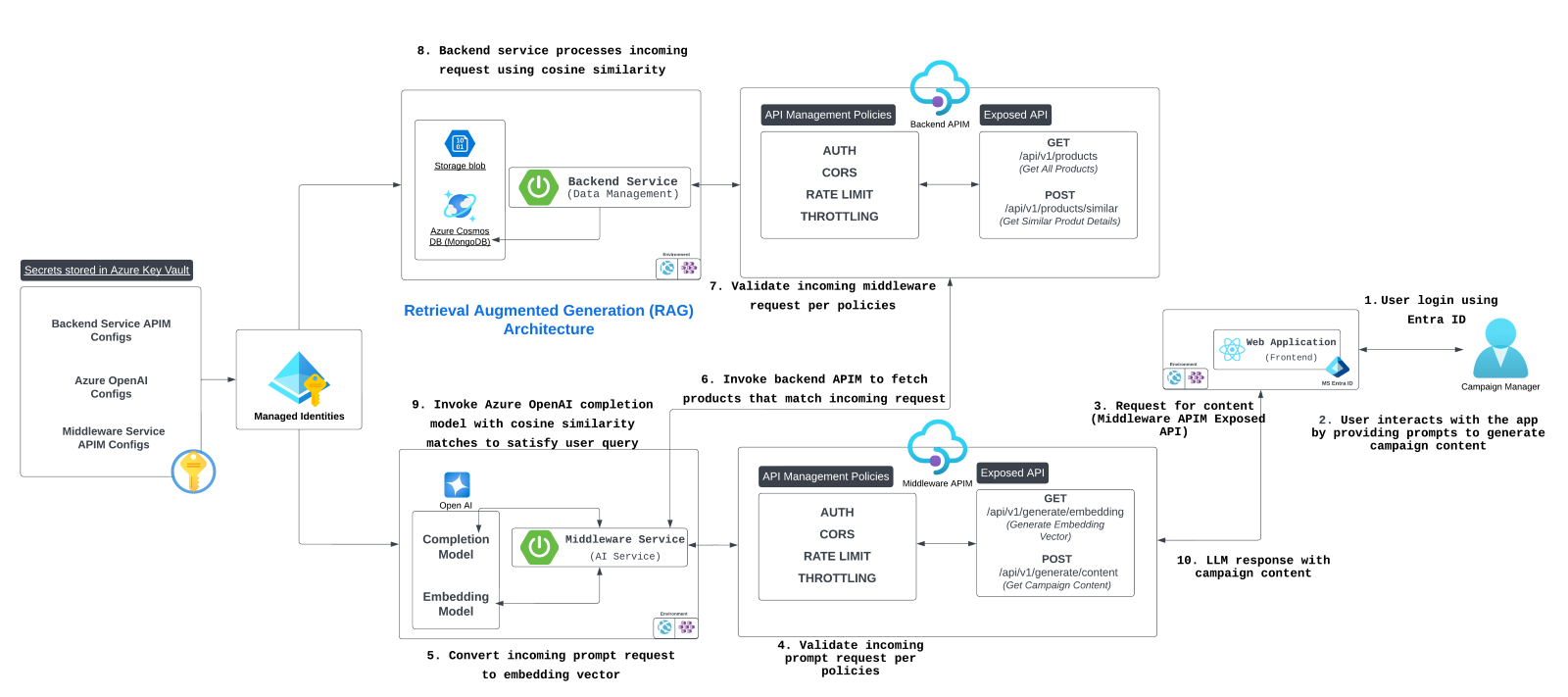
5. Data flow diagram
The data flow diagram shows how the user query flows from the front-end app to the middleware service and finally to the back-end service:
-
User -> Front end. The user submits a query.
-
Front end -> Middleware API Management endpoint. The query is sent to the middleware via API Management, which enforces API key checks and security.
-
Middleware -> Back-end API Management endpoint. The middleware sends a vectorized query to the back end via API Management.
-
Back-end -> Database. The back end retrieves similar products from Azure Cosmos DB.
-
Middleware -> OpenAI. The middleware generates content using OpenAI’s models.
-
Middleware -> Front end. The generated content is returned to the front end for display.
Learn more on Technical leaders’ guide to building intelligent apps.
Summary
In today’s blog post, we discussed the inner workings of our example AI-based content generation app, detailing the interactions between the front-end, middleware, and back-end app tiers. We learned how our app uses various Azure services, like Azure API Management, Azure Key Vault, Azure Cosmos DB, Azure Blob Storage, and Azure OpenAI Service to build a secure and scalable solution.
In the next post—the last in this series—we'll explore the outcomes of building this application, highlighting its scalability and performance, the overall impact of the architecture and technologies used, and the key learnings to take away from the project.
