Deploy only Service Health Alerts
Updating from the preview version isn’t supported. If you deployed the preview version, proceed with Moving from preview to GA before continuing.
The following guide describes the steps to use the ALZ pattern to implement Service Health Alerts. When you deploy one Policy Set Definition, like Service Health, you will only need the Policy Definitions required by that Policy Set Definition. You can still choose to deploy all Policy Definitions that are provided in the ALZ Pattern, this is recommended when you want to deploy other Policy Set Definitions in the future. In case you first deploy a subset of the Policy Definitions, you can easily deploy additional definitions at a later stage. This document covers two deployment options:
- Quick Deployment: Deploys the ALZ Pattern including all Policy Definitions, Policy Set Definitions, however, this assigns only the Service Health Policy Set Definition.
- Custom Deployment: Deploys only the Policy Definitions and Policy Set Definition that are needed for the Service Health Alerts. Assigns only the Service Health Policy Set Definition.
In this example we will deploy the Service Health Policy Set Definition via Azure CLI. However, the same principles and steps apply to other Policy Set Definitions and deployment methods as well.
To start, you can either download a copy of the parameter file or clone/fork the repository.
The following changes apply to all scenarios, whether you are aligned or unaligned with ALZ or have a single management group.
Change the value of the following parameters at the beginning of parameter file according to the instructions below:
While it’s technically possible to not add any notification information (no email, no ARM Role, no Logic App, etc.) it is strongly recommended to configure at least one option.- Change the value of
enterpriseScaleCompanyPrefixto the management group where you wish to deploy the policies and the initiatives. This is usually the so called “pseudo root management group”, for example, in ALZ terminology, this would be the so called “Intermediate Root Management Group” (directly beneath the “Tenant Root Group”).
- Change the value of
Change the value of parameters under the
policyAssignmentParametersCommonaccording to the instructions below:- Change the value of
ALZMonitorResourceGroupNameto the name of the resource group where the activity logs, resource health alerts, actions groups and alert processing rules will be deployed in. - Change the value of
ALZMonitorResourceGroupTagsto specify the tags to be added to said resource group. - Change the value of
ALZMonitorResourceGroupLocationto specify the location for said resource group.
- Change the value of
Change the value of parameters under the
policyAssignmentParametersNotificationAssetsaccording to the instructions below:Change the value of
ALZMonitorActionGroupEmailto the email address(es) where notifications of the alerts (including Service Health alerts) are sent to. Leave the value blank if no email notification is used.Change the value of
ALZLogicappResourceIdto the Logic app resource id to be used as action for the alerts (including Service Health alerts). Leave the value blank if no Logic app is used.Change the value of
ALZLogicappCallbackUrlto the Logic app callback url of the Logic app you want to use as action for the alerts (including Service Health alerts). Leave the value blank if no Logic app is used. To retrieve the callback url you can either use the Get-AzLogicAppTriggerCallbackUrl PowerShell command or navigate to the Logic app in the Azure portal, go to Logic app designer, expand the trigger activity (When an HTTP request is received) and copy the value in the URL field using the 2-sheets icon.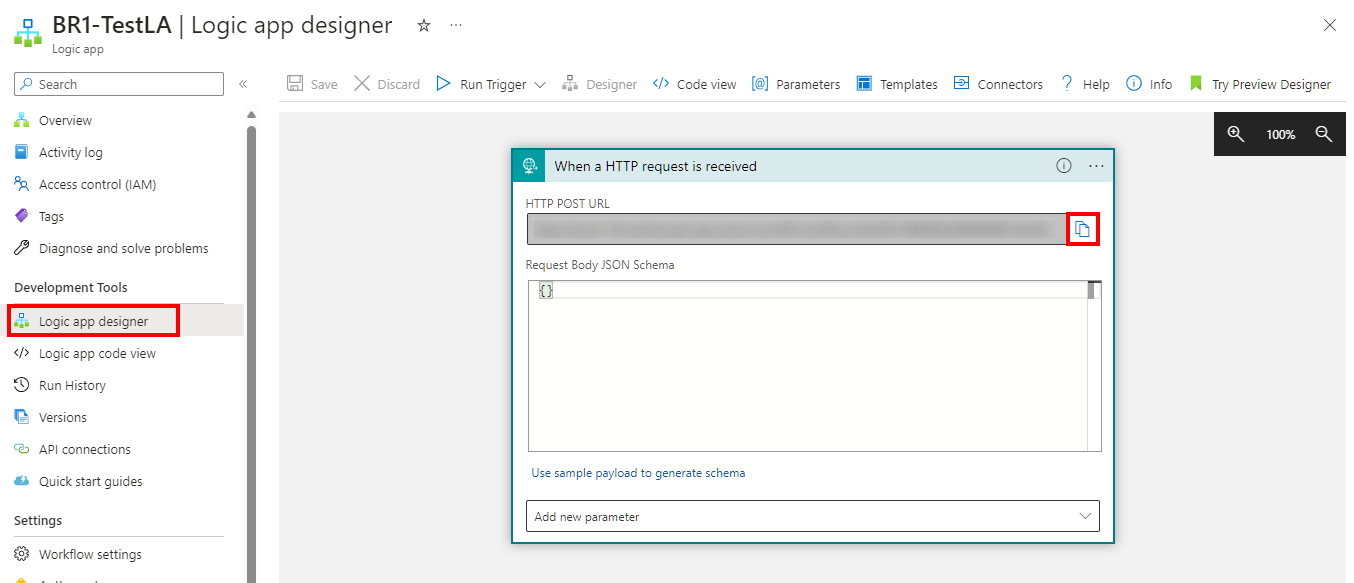
Change the value of
ALZArmRoleIdto the Azure Resource Manager Role(s) where notifications of the alerts (including Service Health alerts) are sent to. Leave the value blank if no Azure Resource Manager Role notification is required.Change the value of
ALZEventHubResourceIdto the Event Hubs to be used as action for the alerts (including Service Health alerts). Leave the value blank if no Event Hubs is used.Change the value of
ALZWebhookServiceUrito the URI(s) to be used as action for the alerts (including Service Health alerts). Leave the value blank if no Webhook is used.Change the value of
ALZFunctionResourceIdto the Function resource id to be used as action for the alerts (including Service Health alerts). Leave the value blank if no Function is used.Change the value of
ALZFunctionTriggerUrlto the Function App trigger url of the function to be used as action for the alerts (including Service Health alerts). Leave the value blank if no Function is used. To retrieve the Function App trigger url with the corresponding code, navigate to the HTTP-triggered functions in the Azure portal, go to Code + Test, select Get function URL from the menu top menu and copy the value in the URL field using the 2-sheets icon.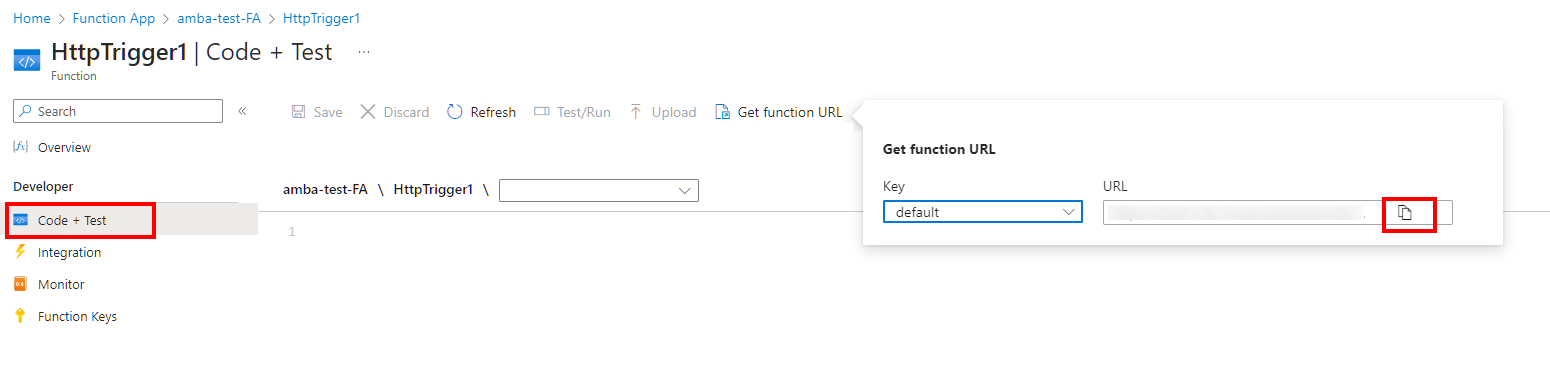
It is possible use multiple email addresses, as well as multiple Arm Roles, Webhooks or Event Hubs (not recommended as per ALZ guidance). Should you set multiple entries, make sure they are entered as single string with values separated by comma. Example:
"ALZMonitorActionGroupEmail": { "value": "action1@contoso.com , action2@contoso.com , action3@contoso.com" }, "ALZArmRoleId": { "value": "8e3af657-a8ff-443c-a75c-2fe8c4bcb635, b24988ac-6180-42a0-ab88-20f7382dd24c" }, "ALZWebhookServiceUri": { "value": "https://webhookUri1.webhook.com, http://webhookUri2.webhook.com" },If you would like to disable initiative assignments, you can change the value on one or more of the following parameters;
enableAMBAConnectivity,enableAMBAIdentity,enableAMBALandingZone,enableAMBAManagement,enableAMBAServiceHealthto “No”.
- Change the value of
platformManagementGroupto the management group id for Platform. - Change the value of
IdentityManagementGroupto the management group id for Identity. - Change the value of
managementManagementGroupto the management group id for Management. - Change the value of
connectivityManagementGroupto the management group id for Connectivity. - Change the value of
LandingZoneManagementGroupto the management group id for Landing Zones.
- Change the value of
platformManagementGroupto the management group id for Platform. The same management group id may be repeated. - Change the value of
IdentityManagementGroupto the management group id for Identity. The same management group id may be repeated. - Change the value of
managementManagementGroupto the management group id for Management. The same management group id may be repeated. - Change the value of
connectivityManagementGroupto the management group id for Connectivity. The same management group id may be repeated. - Change the value of
LandingZoneManagementGroupto the management group id for Landing Zones. The same management group id may be repeated.
For ease of deployment and maintenance we have kept the same variables. For example, if you combined Identity, Management and Connectivity into one management group you should configure the variablesidentityManagementGroup,managementManagementGroup,connectivityManagementGroupandLZManagementGroupwith the same management group id.
- Change the value of
platformManagementGroupto the pseudo root management group id, also called the “Intermediate Root Management Group”. - Change the value of
IdentityManagementGroupto the pseudo root management group id, also called the “Intermediate Root Management Group”. - Change the value of
managementManagementGroupto the pseudo root management group id, also called the “Intermediate Root Management Group”. - Change the value of
connectivityManagementGroupto the pseudo root management group id, also called the “Intermediate Root Management Group”. - Change the value of
LandingZoneManagementGroupto the pseudo root management group id, also called the “Intermediate Root Management Group”.
For ease of deployment and maintenance we have kept the same variables. Configure the variablesenterpriseScaleCompanyPrefix,identityManagementGroup,managementManagementGroup,connectivityManagementGroupandLZManagementGroupwith the pseudo root management group id.
The parameter file shown below has been truncated for brevity, compared to the samples included.
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentParameters.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"parameters": {
"enterpriseScaleCompanyPrefix": {
"value": "contoso"
},
"platformManagementGroup": {
"value": "contoso-platform"
},
"IdentityManagementGroup": {
"value": "contoso-identity"
},
"managementManagementGroup": {
"value": "contoso-management"
},
"connectivityManagementGroup": {
"value": "contoso-connectivity"
},
"LandingZoneManagementGroup": {
"value": "contoso-landingzones"
},
"enableAMBAConnectivity": {
"value": "No"
},
"enableAMBAIdentity": {
"value": "No"
},
"enableAMBALandingZone": {
"value": "No"
},
"enableAMBAManagement": {
"value": "No"
},
"enableAMBAServiceHealth": {
"value": "Yes"
},
"policyAssignmentParametersCommon": {
"value": {
"ALZMonitorResourceGroupName": {
"value": "rg-amba-monitoring-001"
},
"ALZMonitorResourceGroupTags": {
"value": {
"Project": "amba-monitoring"
}
},
"ALZMonitorResourceGroupLocation": {
"value": "eastus"
}
}
}
}
}
Open your preferred command-line tool (Windows PowerShell, Cmd, Bash or other Unix shells), and navigate to the root of the cloned repo and log on to Azure with an account with at least Resource Policy Contributor access at the root of the management group hierarchy where you will be creating the policies and Policy Set Definitions.
Run the following commands:
location="Your Azure location of choice"
pseudoRootManagementGroup="The pseudo root management group id parenting the identity, management and connectivity management groups"
When running Azure CLI from PowerShell the variables have to start with a $.
Above-mentioned
pseudoRootManagementGroupvariable value, being the so called “pseudo root management group id”, should coincide with the value of theenterpriseScaleCompanyPrefixparameter, as set previously within the parameter files.The
locationvariable refers to the deployment location. Deploying to multiple regions is not necessary as the definitions and assignments are scoped to a management group and are not region-specific.
Using your preferred command-line tool (Windows PowerShell, Cmd, Bash or other Unix shells), if you closed your previous session, navigate again to the root of the cloned repo and log on to Azure with an account with at least Resource Policy Contributor access at the root of the management group hierarchy where you will be creating the policies and Policy Set Definitions.
az deployment mg create --template-uri https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/azure-monitor-baseline-alerts/2024-03-01/patterns/alz/alzArm.json --name "amba-GeneralDeployment" --location $location --management-group-id $pseudoRootManagementGroup --parameters .\patterns\alz\alzArm.param.json
To create a copy of a Bicep policy file (policies.bicep), you can use standard file copying techniques based on your operating system and programming language of choice. For example, run the following command in PowerShell:
Copy-Item -Path .\patterns\alz\templates\policies.bicep -Destination .\patterns\alz\templates\policies-sh.bicep
Open the newly created Bicep file in your favorite text editor, such as Visual Studio Code (VS Code). Edit the variables loadPolicyDefinitions and loadPolicySetDefinitions in your Bicep file to include only the relevant policy definitions. You should delete or comment out the unnecessary lines. In bicep use // to comment a line. The example below shows the lines you need to keep for the Service Health Policy Set Definition.
loadPolicyDefinitions variable
{
var loadPolicyDefinitions = {
All: [
loadTextContent('../../../services/Resources/subscriptions/Deploy-ServiceHealth-ActionGroups.json')
loadTextContent('../../../services/Resources/subscriptions/Deploy-ActivityLog-ResourceHealth-UnHealthly-Alert.json')
loadTextContent('../../../services/Resources/subscriptions/Deploy-ActivityLog-ServiceHealth-Health.json')
loadTextContent('../../../services/Resources/subscriptions/Deploy-ActivityLog-ServiceHealth-Incident.json')
loadTextContent('../../../services/Resources/subscriptions/Deploy-ActivityLog-ServiceHealth-Maintenance.json')
loadTextContent('../../../services/Resources/subscriptions/Deploy-ActivityLog-ServiceHealth-Security.json')
]
AzureCloud: []
AzureChinaCloud: []
AzureUSGovernment: []
}
}
loadPolicySetDefinitions variable
var loadPolicySetDefinitions = {
All: [
loadTextContent('../policySetDefinitions/Deploy-ServiceHealth-Alerts.json')
]
AzureCloud: []
AzureChinaCloud: []
AzureUSGovernment: []
}
To compile your Bicep file and generate the corresponding JSON ARM template file, you can use the bicep build command. Follow these steps:
bicep build .\patterns\alz\templates\policies-sh.bicep --outfile .\patterns\alz\policyDefinitions\policies-sh.json
Make sure you have the Bicep CLI installed and configured in your environment before running this command.
Open your preferred command-line tool (Windows PowerShell, Cmd, Bash or other Unix shells), and navigate to the root of the cloned repo and log on to Azure with an account with at least Resource Policy Contributor access at the root of the management group hierarchy where you will be creating the policies and Policy Set Definitions.
Run the following commands:
location="Your Azure location of choice"
pseudoRootManagementGroup="The pseudo root management group id parenting the identity, management and connectivity management groups"
When running Azure CLI from PowerShell the variables have to start with a $.
Above-mentioned
pseudoRootManagementGroupvariable value, being the so called “pseudo root management group id”, should coincide with the value of theenterpriseScaleCompanyPrefixparameter, as set previously within the parameter files.The
locationvariable refers to the deployment location. Deploying to multiple regions is not necessary as the definitions and assignments are scoped to a management group and are not region-specific.
To deploy policy definitions to the intermediate management group, run the following command:
az deployment mg create --name "amba-ServiveHealthOnly" --template-file .\patterns\alz\policyDefinitions\policies-sh.json --location $location --management-group-id $pseudoRootManagementGroup
Assign a Policy Set Definition by running the following command:
az deployment mg create --name "amba-ServiceHealthAssignment" --template-file .\patterns\alz\policyAssignments\DINE-ServiceHealthAssignment.json --location $location --management-group-id $pseudoRootManagementGroup --parameters '{ \"topLevelManagementGroupPrefix\": { \"value\": \"contoso\" }, \"policyAssignmentParameters\": { \"value\": { \"ALZMonitorResourceGroupName\": { \"value\": \"rg-amba-monitoring-001\" }, \"ALZMonitorResourceGroupTags\": { \"value\": { \"Project\": \"amba-monitoring\" } }, \"ALZMonitorResourceGroupLocation\": { \"value\": \"eastus\" }, \"ALZMonitorActionGroupEmail\": { \"value\": \"test@test.com\"} } } }'
The final parameter is the
--parametersparameter, which is used to pass a JSON string that contains the parameters for the deployment. The JSON string is enclosed in single quotes and contains escaped double quotes for the keys and values of the parameters.The JSON object contains two parameters:
topLevelManagementGroupPrefixandpolicyAssignmentParameters. ThetopLevelManagementGroupPrefixparameter is used to specify the intermediate root management group, and should coincide with the value of thepseudoRootManagementGroup. ThepolicyAssignmentParametersparameter is an object that contains the values for the parameters that are used to configure the monitoring resource group. The parameters include the name of the resource group, the tags for the resource group, the location of the resource group, and the email address for the action group associated with the Service Health Policy Set Definition.
To remediate non-compliant policies, continue with Policy remediation
