kubernetes-hackfest
Delivering modern cloud-native applications with open source technologies on Azure Kubernetes Service
Module 2: Using global network policies for security controls
Goal: Leverage global network policies to segment connections within the AKS cluster.
Docs: https://projectcalico.docs.tigera.io/reference/resources/globalnetworkpolicy
Steps
-
Test connectivity between application components and across application stacks to establish the baseline behavior; all of these tests should succeed since there are no network policies configured at this stage to govern the traffic for
devanddefaultnamespaces.a. Test connectivity between workloads within each namespace.
# Test connectivity within dev namespace kubectl -n dev exec -t centos -- sh -c 'curl -m3 -sI http://nginx-svc 2>/dev/null | grep -i http' # Test connectivity within default namespace kubectl exec -it $(kubectl get po -l app=loadgenerator -ojsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -- sh -c 'curl -m3 -sI frontend 2>/dev/null | grep -i http' kubectl exec -it $(kubectl get po -l app=frontend -ojsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -c server -- sh -c 'nc -zv productcatalogservice 3550'b. Test connectivity across namespaces.
# Test connectivity from dev namespace to default namespace kubectl -n dev exec -t centos -- sh -c 'curl -m3 -sI http://frontend.default 2>/dev/null | grep -i http' # Test connectivity from default namespace to dev namespace kubectl exec -it $(kubectl get po -l app=loadgenerator -ojsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -- sh -c 'curl -m3 -sI http://nginx-svc.dev 2>/dev/null | grep -i http'c. Test connectivity from each namespace to the Internet.
# Test connectivity from dev namespace to the Internet kubectl -n dev exec -t centos -- sh -c 'curl -m3 -sI http://www.bing.com 2>/dev/null | grep -i http' # Test connectivity from default namespace to the Internet kubectl exec -it $(kubectl get po -l app=loadgenerator -ojsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -- sh -c 'curl -m3 -sI www.bing.com 2>/dev/null | grep -i http' -
Apply network policies to control East-West traffic, including kubernetes policies for demo pods in
devnamespace and calico policies for mircoservices of boutiqueshop indefaultnamespaces.# Deploy dev policies kubectl apply -f demo/dev/policies.yaml # Deploy boutiqueshop policies, you will need use --allow-version-mismatch to override if client/cluster version mismatch. calicoctl --allow-version-mismatch apply -f demo/boutiqueshop/policies.yamlNow as we have proper policies in place, we can deploy
default-denyas global network policy moving closer to zero-trust security approach.# Apply enforcing default-deny policy manifest calicoctl --allow-version-mismatch apply -f demo/10-security-controls/default-deny.yamlNote: The
default-denypolicy includes global egress policy which allow all namespaces to communicate to kube-dns pods. - Test connectivity with policies in place. Expected Outcome:
- Connections between components in a single namespace should be allowed
- Cross-namespace and Internet connections should be denied
This is the connection after we have network policy in place.
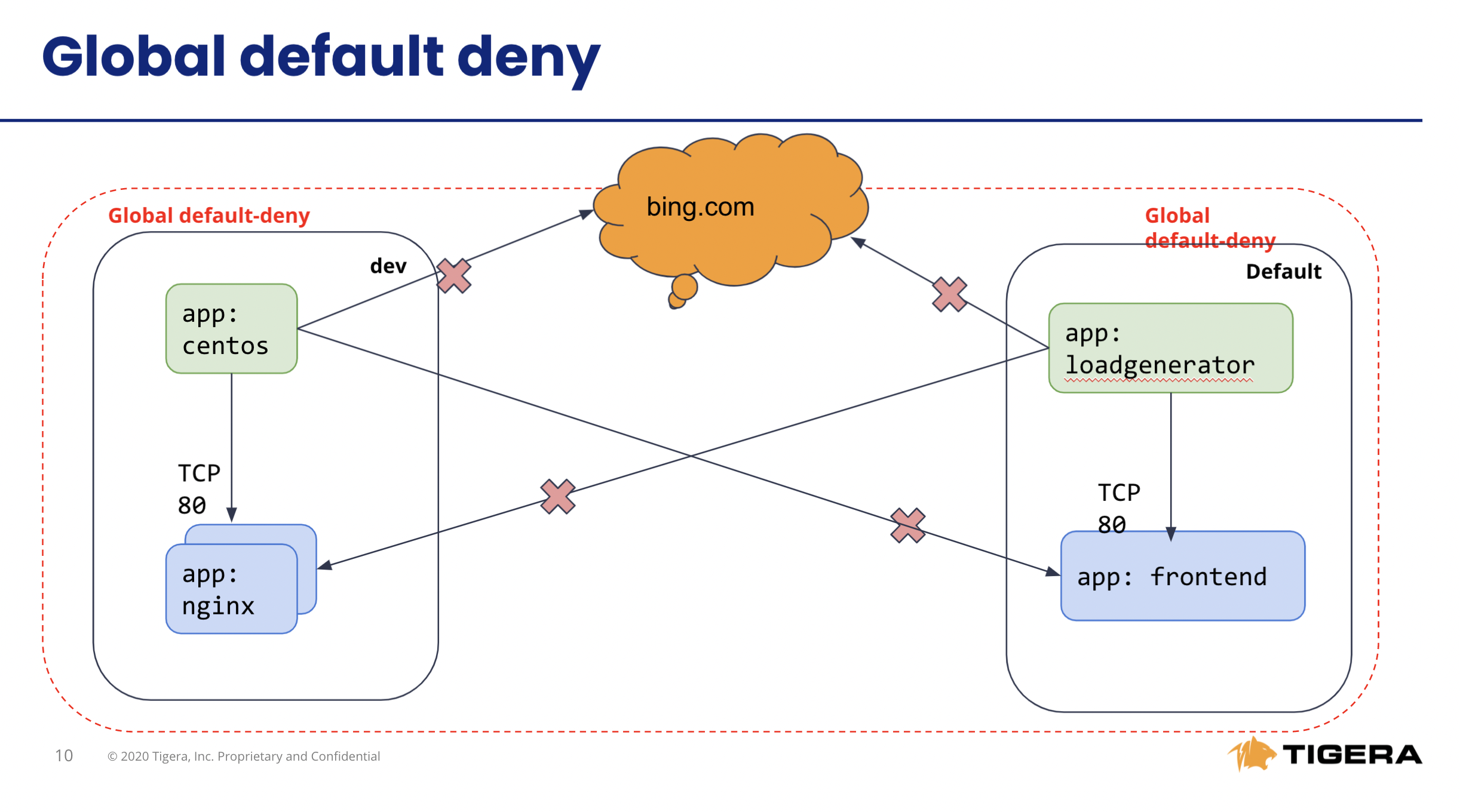
a. The only connections between components within each namespaces should be allowed as configured by the policies.
# Test connectivity within dev namespace kubectl -n dev exec -t centos -- sh -c 'curl -m3 -sI http://nginx-svc 2>/dev/null | grep -i http' # Test connectivity within default namespace kubectl exec -it $(kubectl get po -l app=loadgenerator -ojsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -- sh -c 'curl -m3 -sI frontend 2>/dev/null | grep -i http'b. The connections across
devanddefaultnamespaces should be blockedwith exit code 1by the globaldefault-denypolicy.# Test connectivity from dev namespace to default namespace kubectl -n dev exec -t centos -- sh -c 'curl -m3 -sI http://frontend.default 2>/dev/null | grep -i http' # Test connectivity from default namespace to dev namespace kubectl exec -it $(kubectl get po -l app=loadgenerator -ojsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -- sh -c 'curl -m3 -sI http://nginx-svc.dev 2>/dev/null | grep -i http'c. The connections to the Internet should be blocked
with exit code 1by the configured policies.# Test connectivity from dev namespace to the Internet kubectl -n dev exec -t centos -- sh -c 'curl -m3 -sI http://www.bing.com 2>/dev/null | grep -i http' # Test connectivity from default namespace to the Internet kubectl exec -it $(kubectl get po -l app=loadgenerator -ojsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -- sh -c 'curl -m3 -sI www.bing.com 2>/dev/null | grep -i http' - Implement egress policy to allow egress access from a workload in one namespace, e.g.
dev/centos, to a service in another namespace, e.g.default/frontend. Expected Outcome:- Connections between components in a single namespace should be allowed
- Cross-namespace
dev/centostodefault/frontendshould be allow, - Internet connections should be denied
a. Deploy egress policy.
calicoctl --allow-version-mismatch create -f demo/20-egress-access-controls/default-centos-to-frontend.yamlb. Test connectivity between
dev/centospod anddefault/frontendservice. The access should be allowed once the egress policy is in place.kubectl -n dev exec -t centos -- sh -c 'curl -m3 -sI http://frontend.default 2>/dev/null | grep -i http'Output will be like this:
HTTP/1.1 200 OKc. Test the connectivity to the Internet, should be same as blocked
with exit code 1by default deny policy.# Test connectivity from dev namespace to the Internet kubectl -n dev exec -t centos -- sh -c 'curl -m3 -sI http://www.bing.com 2>/dev/null | grep -i http' # Test connectivity from default namespace to the Internet kubectl exec -it $(kubectl get po -l app=loadgenerator -ojsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -- sh -c 'curl -m3 -sI www.bing.com 2>/dev/null | grep -i http'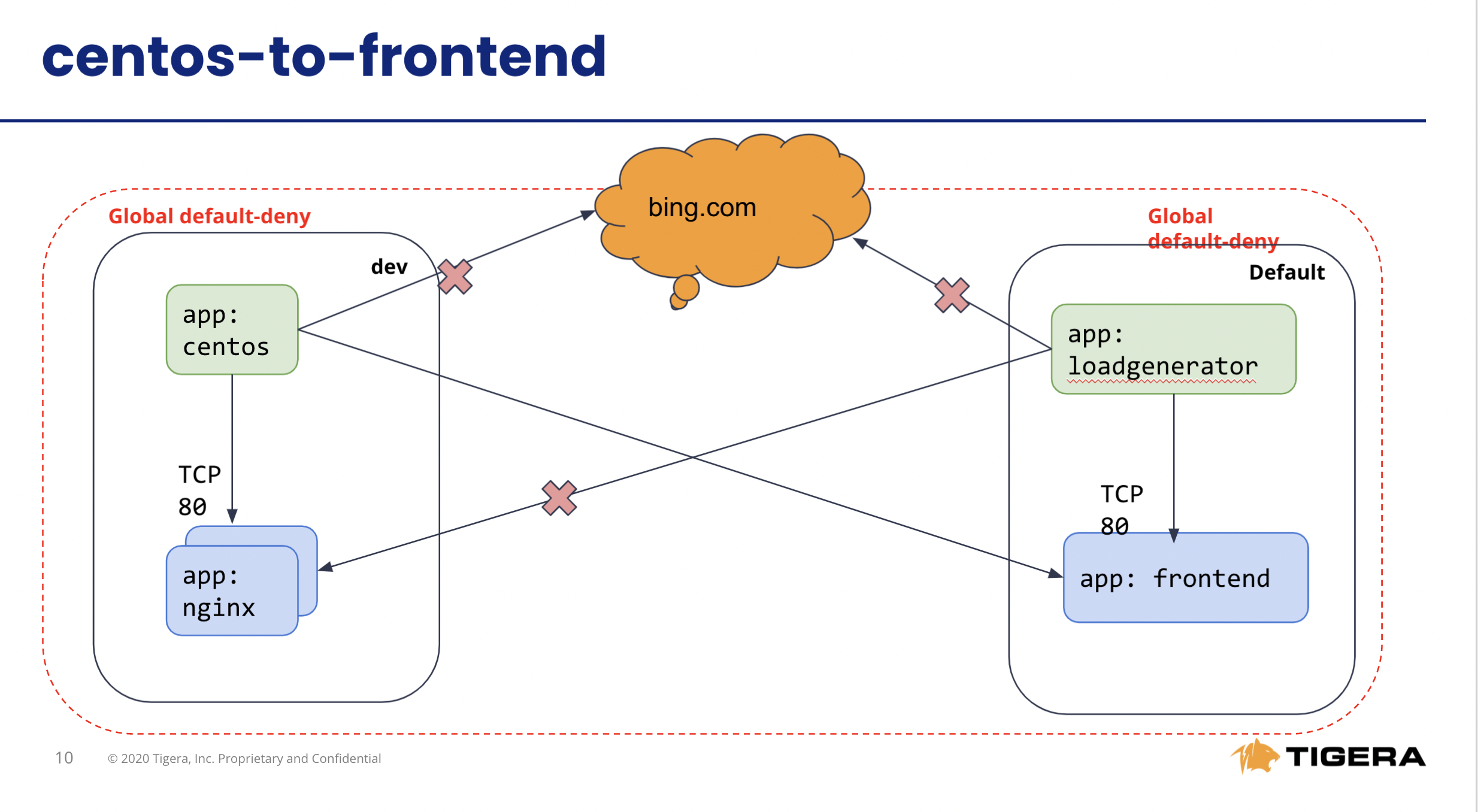
Calico Cloud & Calico EE offer a DNS policy feature, which can whitelist DNS domains, such as www.bing.com, we will test this feature in next Chapter.