DecoderSample
This sample allows you to create and run your own LoRa message decoder in an independent container running on your LoRa gateway without having to edit the main LoRa Engine. This description shows you how to get started.
Customizing
To add a new decoder, simply copy or reuse the sample DecoderValueSensor method from the LoraDecoders class in LoraDecoder.cs. You can name the method whatever you like and can create as many decoders as you need by adding new, individual methods to the LoraDecoders class.
The payload sent to the decoder is passed as string devEui, byte[] payload and uint fport.
After writing the code that decodes your message, your method should return a string containing valid JSON containing the response to be sent upstream.
internal static class LoraDecoders
{
private static string DecoderValueSensor(string devEUI, byte[] payload, byte fport)
{
// EITHER: Convert a payload containing a string back to string format for further processing
var result = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(payload);
// OR: Convert a payload containing binary data to HEX string for further processing
var result_binary = ConversionHelper.ByteArrayToString(payload);
// Write code that decodes the payload here.
// Return a JSON string containing the decoded data
return JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new { value = result });
}
}
You can test the decoder on your machine by debugging the SensorDecoderModule project in Visual Studio.
When creating a debugging configuration in Visual Studio Code or a launchSettings.json file in Visual Studio, the default address that the webserver will try to use is http://localhost:5000 or https://localhost:5001. You can override this with any port of your choice.
On launching the debugger you will see a webbrowser with a 404 Not Found error as there is no default document to be served in this Web API app.
You will also manually need to base64-encode and URL-encode the payload before adding it to the URL parameters.
For example, to test a payload of ABCDE12345, you:
- Convert it to a base64 encoded string:
QUJDREUxMjM0NQ== - Convert the result to a valid URL parameter:
QUJDREUxMjM0NQ%3D%3D - Add this to your test URL.
For the built-in sample decoder DecoderValueSensor with Visual Studio (Code)'s default settings this would be:
http://localhost:5000/api/DecoderValueSensor?devEui=0000000000000000&fport=1&payload=QUJDREUxMjM0NQ%3D%3D
You can call your decoder at:
http://localhost:yourPort/api/<decodername>?devEui=0000000000000000&fport=1&payload=<QUJDREUxMjM0NQ%3D%3D>
You should see the result as JSON string.

When running the solution in a container, the Kestrel webserver from .NET Core uses the HTTP default port 80 of the container and does not need to bind it to a port on the host machine as Docker allows for container-to-container communication. IoT Edge automatically creates the required Docker Network Bridge.
Preparing and Testing the Docker Image
Create a docker image from your finished solution based on the target architecture and host it in an Azure Container Registry, on DockerHub or in any other container registry of your choice.
We are using the Azure IoT Edge for Visual Studio Code extension to build and push the Docker image.
Make sure you are logged in to the Azure Container Registry you are using. Run docker login <mycontainerregistry>.azurecr.io on your development machine.
Edit the file module.json to contain your container registry address, image name and version number:

We provide the Dockerfiles for the following architectures:
To build the Docker image, right-click on the module.json file and select "Build IoT Edge Module Image" or "Build and Push IoT Edge Module Image". Select the architecture you want to build for (ARM32v7 or AMD64) from the drop-down menu.
To temporarily test the container running you decoder using a webbrowser or Postman, you can manually start it in Docker and bind the container's port 80 to a free port on your host machine, like for example 8881.
docker run --rm -it -p 8881:80 --name decodersample <container registry>/<image>:<tag>
````
You can then use a browser to navigate to:
### Deploying to IoT Edge
If required, add credentials to access your container registry to the IoT Edge device by adding them to IoT Hub → IoT Edge → Your Device → Set Modules → Container Registry settings.
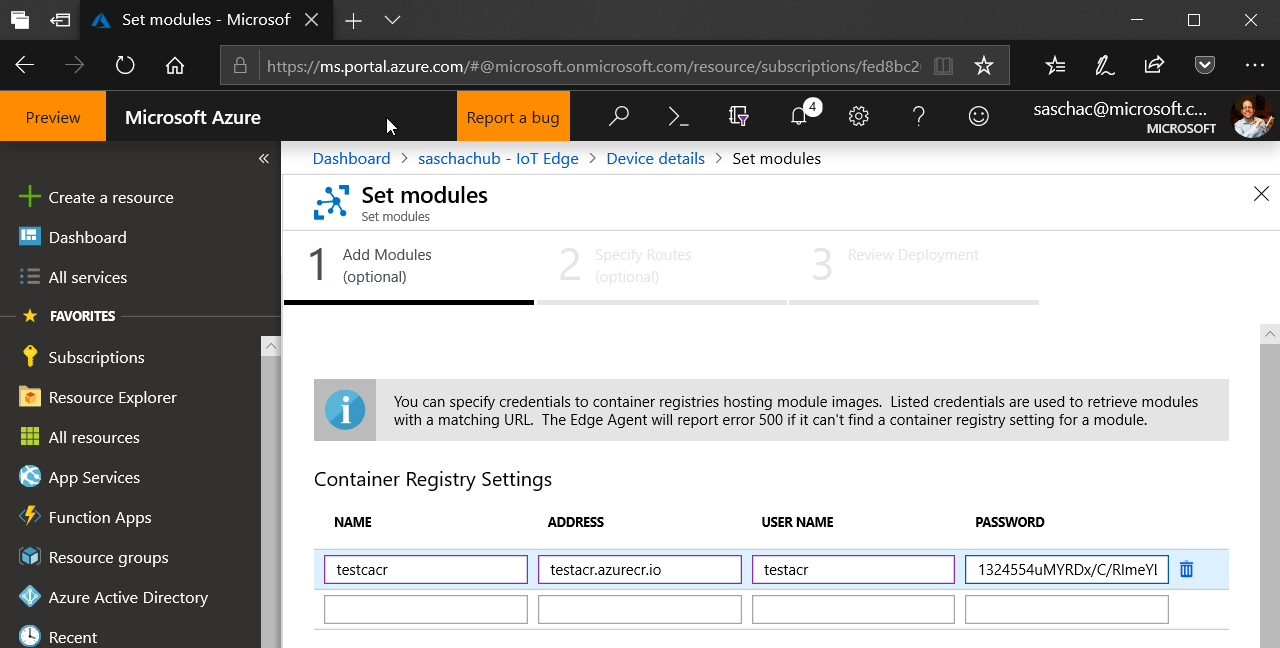
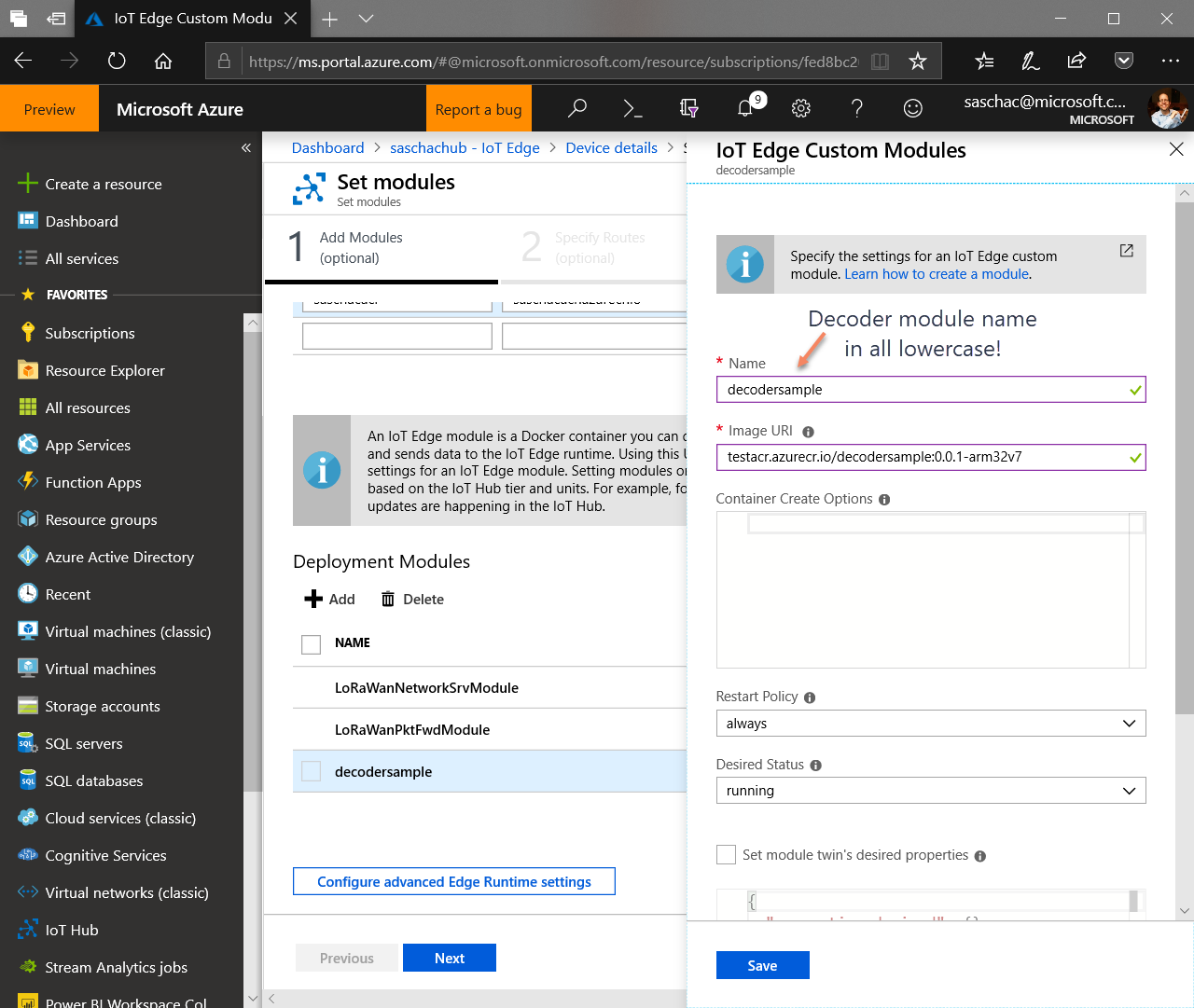
Configure your IoT Edge gateway device to include the custom container. IoT Hub → IoT Edge → Your Device → Set Modules → Deployment Modules → Add → IoT Edge Module. Set the module Name and Image URI, pointing to your image created above.
**Make sure to choose all lowercase letters for the Module Name as the container will be unreachable otherwise!**
To activate the decoder for a LoRa device, navigate to your IoT Hub → IoT Devices → Device Details → Device Twin and set the ```SensorDecoder``` value in the desired properties to:
Again make sure to chosse all lowercase letters for the module name to make sure it is reachable.

In case the custom decoder is unreachable, throws an error or return invalid JSON, the error message will be shown in your device's messages in IoT Hub.