High-level contribution flow
---
config:
nodeSpacing: 20
rankSpacing: 20
diagramPadding: 50
padding: 5
flowchart:
wrappingWidth: 300
padding: 5
layout: elk
elk:
mergeEdges: true
nodePlacementStrategy: LINEAR_SEGMENTS
---
flowchart TD
A(1 - Fork the module source repository)
click A "/Azure-Verified-Modules/contributing/terraform/terraform-contribution-flow/#1-fork-the-module-source-repository"
B(2 - Setup your Azure test environment)
click B "/Azure-Verified-Modules/contributing/terraform/terraform-contribution-flow/#2-prepare-your-azure-test-environment"
C(3 - Implement your contribution)
click C "/Azure-Verified-Modules/contributing/terraform/terraform-contribution-flow/#3-implement-your-contribution"
D{4 - Pre-commit<br>checks successful?}
click D "/Azure-Verified-Modules/contributing/terraform/terraform-contribution-flow/#4-run-pre-commit-checks"
E(5 - Create a pull request to the upstream repository)
click E "/Azure-Verified-Modules/contributing/terraform/terraform-contribution-flow/#5-create-a-pull-request-to-the-upstream-repository"
F(6 - Get your pull request approved)
click F "/Azure-Verified-Modules/contributing/terraform/terraform-contribution-flow/#6-get-your-pull-request-approved"
A --> B
B --> C
C --> D
D -->|yes|E
D -->|no|C
E --> F
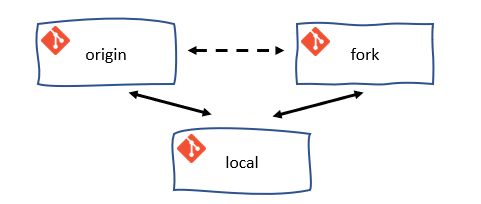
GitFlow for contributors
The GitFlow process outlined here depicts and suggests a way of working with Git and GitHub. It serves to synchronize the forked repository with the original upstream repository. It is not a strict requirement to follow this process, but it is highly recommended to do so.
---
config:
logLevel: debug
gitGraph:
rotateCommitLabel: false
---
gitGraph LR:
commit id:"fork"
branch fork/main
checkout fork/main
commit id:"checkout feature" type: HIGHLIGHT
branch feature
checkout feature
commit id:"checkout fix"
branch fix
checkout main
merge feature id: "Pull Request 'Feature'" type: HIGHLIGHT
checkout fix
commit id:"Patch 1"
commit id:"Patch 2"
checkout main
merge fix id: "Pull Request 'Fix'" type: HIGHLIGHT
Tip
When implementing the GitFlow process as described, it is advisable to configure the local clone of your forked repository with an additional remote for the upstream repository. This will allow you to easily synchronize your locally forked repository with the upstream repository. Remember, there is a difference between the forked repository on GitHub and the clone of the forked repository on your local machine.

Note
Each time in the following sections we refer to ‘your xyz’, it is an indicator that you have to change something in your own environment.
Prepare your developer environment
1. Fork the module source repository
Important
Each Terraform AVM module will have its own GitHub repository in the Azure GitHub Organization as per SNFR19.
This repository will be created by the Module owners and the AVM Core team collaboratively, including the configuration of permissions as per SNFR9
Module contributors are expected to fork the corresponding repository and work on a branch from within their fork, before then creating a Pull Request (PR) back into the source repository’s main branch.
To do so, simply navigate to your desired repository, select the 'Fork' button to the top right of the UI, select where the fork should be created (i.e., the owning organization) and finally click ‘Create fork’.
Note
If the module repository you want to contribute to is not yet available, please get in touch with the respective module owner which can be tracked in the Terraform Resource Modules index see PrimaryModuleOwnerGHHandle column.
Optional: The usage of local source branches
For consistent contributors but also Azure-org members in general it is possible to get invited as collaborator of the module repository which enables you to work on branches instead of forks. To get invited get in touch with the module owner since it’s the module owner’s decision who gets invited as collaborator.
2. Prepare your Azure test environment
AVM performs end-to-end (e2e) test deployments of all modules in Azure for validation. We recommend you to perform a local e2e test deployment of your module before you create a PR to the upstream repository. Especially because the e2e test deployment will be triggered automatically once you create a PR to the upstream repository.
Have/create an Azure Active Directory Service Principal with at least Contributor & User Access Administrator permissions on the Management-Group/Subscription you want to test the modules in. You might find the following links useful:
# Linux/MacOs
export ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID=$(az account show --query id --output tsv) # or set <subscription_id>
export ARM_TENANT_ID=$(az account show --query tenantId --output tsv) # or set <tenant_id>
export ARM_CLIENT_ID=<client_id>
export ARM_CLIENT_SECRET=<service_principal_password>
# Windows/Powershell
$env:ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID = $(az account show --query id --output tsv) # or set <subscription_id>
$env:ARM_TENANT_ID = $(az account show --query tenantId --output tsv) # or set <tenant_id>
$env:ARM_CLIENT_ID = "<client_id>"
$env:ARM_CLIENT_SECRET = "<service_principal_password>"
Change to the root of your module repository and run ./avm docscheck (Linux/MacOs) / ./avm docscheck (Windows) to verify the container image is working as expected or needs to be pulled first. You will need this later.

3. Implement your contribution
To implement your contribution, we kindly ask you to first review the Terraform specifications and composition guidelines in particular to make sure your contribution complies with the repository’s design and principles.
Tip
To get a head start on developing your module, consider using the tooling recommended per spec TFNFR37. For example you can use the newres tool to help with creating variables.tf and main.tf if you’re developing a module using Azurerm provider.
4. Run Pre-commit Checks
Important
Make sure you have Docker installed and running on your machine.
Note
To simplify and help with the execution of commands like pre-commit, pr-check, docscheck, fmt, test-example, etc. there is now a simplified avm script available distributed to all repositories via terraform-azurerm-avm-template which combines all scripts from the avm_scripts folder in the tfmod-scaffold repository using avmmakefile.
The avm script also makes sure to pull the latest mcr.microsoft.com/azterraform:latest container image before executing any command.
4.1. Run pre-commit and pr-check
The following commands will run all pre-commit checks and the pr-check.
# Running all pre-commit checks
# `pre-commit` runs depsensure fmt fumpt autofix docs
# `pr-check` runs fmtcheck tfvalidatecheck lint unit-test
## Linux/MacOs
./avm pre-commit
./avm pr-check
## Windows
./avm pre-commit
./avm pr-check
4.2 Run e2e tests
Currently you have two options to run e2e tests:
Note
With the help of the avm script and the commands ./avm test-example (Linux/MacOs) / ./avm test-example (Windows) you will be able to run it in a more simplified way. Currently the test-example command is not completely ready yet and will be released soon. Therefore please use the below docker command for now.
Run e2e tests with the help of the azterraform docker container image.
# Linux/MacOs
docker run --rm -v $(pwd):/src -w /src -v $HOME/.azure:/root/.azure -e TF_IN_AUTOMATION -e AVM_MOD_PATH=/src -e AVM_EXAMPLE=<example_folder> -e ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID -e ARM_TENANT_ID -e ARM_CLIENT_ID -e ARM_CLIENT_SECRET mcr.microsoft.com/azterraform:latest make test-example
# Powershell
docker run --rm -v ${pwd}:/src -w /src -v $HOME/.azure:/root/.azure -e TF_IN_AUTOMATION -e AVM_MOD_PATH=/src -e AVM_EXAMPLE=<example_folder> -e ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID -e ARM_TENANT_ID -e ARM_CLIENT_ID -e ARM_CLIENT_SECRET mcr.microsoft.com/azterraform:latest make test-example
Make sure to replace <client_id> and <service_principal_password> with the values of your service principal as well as <example_folder> (e.g. default) with the name of the example folder you want to run e2e tests for.
Run e2e tests with the help of terraform init/plan/apply.
Simply run terraform init and terraform apply in the example folder you want to run e2e tests for. Make sure to set the environment variables ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID, ARM_TENANT_ID, ARM_CLIENT_ID and ARM_CLIENT_SECRET before you run terraform init and terraform apply or make sure you have a valid Azure CLI session and are logged in with az login.
5. Create a pull request to the upstream repository
Once you are satisfied with your contribution and validated it, submit a pull request to the upstream repository and work with the module owner to get the module reviewed by the AVM Core team, by following the initial module review process for Terraform Modules, described here. This is a prerequisite for publishing the module. Once the review process is complete and your PR is approved, merge it into the upstream repository and the Module owner will publish the module to the HashiCorp Terraform Registry.
5.1 Create the Pull Request [Contributor]
These steps are performed by the contributor:
- Navigate to the upstream repository and click on the
Pull requests tab. - Click on the
New pull request button. - Ensure the
base repository is set to the upstream AVM repo. - Ensure the
base branch is set to main. - Ensure your
head repository and compare branch are set to your fork and the branch you are working on. - Click on the
Create pull request button.
5.2 Review the Pull Request [Owner]
- IMPORTANT: The module owner must first check for any malicious code or changes to workflow files. If they are found, the owner should close the PR and report the contributor.
- Review the changes made by the contributor and determine whether end to end tests need to be run.
- If end to end tests do not need to be run (e.g. doc changes, small changes, etc) then so long as the static analysis passes, the PR can be merged to main.
- If end to end tests do need to be run, then follow the steps in 5.3.
5.3 Release Branch and Run End to End Tests [Owner]
- IMPORTANT: The module owner must first check for any malicious code or changes to workflow files. If they are found, the owner should close the PR and report the contributor.
- Create a release branch from
main. Suggested naminmg convention is release/<description-of-change>. - Open the PR created by the contributor and click
Edit at the top right of the PR. - Change the
base branch to the release branch you just created. - Wait for the PR checks to run, validate the code looks good and then merge the PR into the release branch.
- Create a new PR from the release branch to the
main branch of the AVM module. - The end to end tests should trigger and you can approve the run.
- Once the end to end tests have passed, merge the PR into the
main branch. - If the end to end tests fail, investigate the failure. You have two options:
- Work with the contributor to resolve the issue and ask them to submit a new PR from their fork branch to the release branch.
- Re-run the tests and merge to
main. Repeat the loop as required.
- If the issue is a simple fix, resolve it directly in the release branch, re-run the tests and merge to
main.
Common mistakes to avoid and recommendations to follow
- If you contribute to a new module then search and update
TODOs (which are coming with the terraform-azurerm-avm-template) within the code and remove the TODO comments once complete terraform.lock.hcl shouldn’t be in the repository as per the .gitignore file- Update the
support.md file \_header.md needs to be updatedsupport.md needs to be updated- Exclude
terraform.tfvars file from the repository
6. Get your pull request approved
To publish a new module or a new version of an existing module, each Pull Request (PR) MUST be reviewed and approved before being merged and published in the Terraform Registry. A contributor (the submitter of the PR) cannot approve their own PR.
This behavior is assisted by policies, bots, through automatic assignment of the expected reviewer(s) and supporting labels.
Important
As part of the PR review process, the submitter (contributor) MUST address any comments raised by the reviewers and request a new review - and repeat this process until the PR is approved.
Once the PR is merged, the module owner MUST ensure that the related GitHub Actions workflow has successfully published the new version of the module.
6.1. Publishing a new module
When publishing a net new module for the first time ever, the PR MUST be reviewed and approved by a member of the core team.
6.2. Publishing a new version of an existing module
When publishing a new version of an existing module (i.e., anything that is not being published for the first time ever), the PR approval logic is the following:
| PR is submitted by a module owner | PR is submitted by anyone, other than the module owner |
| Module has a single module owner | AVM core team or in case of Terraform only, the owner of another module approves the PR | Module owner approves the PR |
| Module has multiple module owners | Another owner of the module (other than the submitter) approves the PR | One of the owners of the module approves the PR |
For more details, please refer to the Owner Contribution flow section.
Subsections of Contribution Flow
This section describes the contribution flow for module owners who are responsible for creating and maintaining Terraform Module repositories.
Important
This contribution flow is for Module owners only.
As a Terraform Module Owner you need to be aware of the AVM contribution process overview & Terraform specifications (including Interfaces) as as these need to be considered during pull request reviews for the modules you own.
Info
Make sure module authors/contributors tested their module in their environment before raising a PR. The PR uses e2e checks with 1ES agents in the 1ES subscriptions. At the moment their is no read access to the 1ES subscription. Also if more than two subscriptions are required for testing, that’s currently not supported.
1. Owner Activities and Responsibilities
Familiarize yourself with the responsibilities as Module Owner outlined in Team Definitions & RACI and in the TF Issue Triage.
- Watch Pull Request (PR) and issue (questions/feedback) activity for your module(s) in your repository and ensure that PRs are reviewed and merged in a timely manner as outlined in SNFR11.
Info
Make sure module authors/contributors tested their module in their environment before raising a PR. Also because once a PR is raised a e2e GitHib workflow pipeline is required to be run successfully before the PR can be merged. This is to ensure that the module is working as expected and is compliant with the AVM specifications.
2. GitHub repository creation and configuration
Once your module has been approved and you are ready to start development, you need to create your new repository.
Follow the Repository Creation Process to create your new repository.
3. Module Development Activities
You can now start developing your module, following standard guidance for Terraform module development.
Some useful things to know:
Pull Request
You can raise a pull request anytime, don’t wait until the end of the development cycle. Raise the PR after you first push your branch.
You can then use the PR to run end to end tests, check linting, etc.
Once ready for review, you can request a review per step 4.
Grept
Grept is a linting tool for repositories, ensures predefined standards, maintains codebase consistency, and quality.
It’s using the grept configuration files from the Azure-Verified-Modules-Grept repository.
You can see here which files are synced from the terraform-azurerm-avm-template repository.
Set environment variables and run Grept:
export GITHUB_REPOSITORY_OWNER=Azure
export GITHUB_REPOSITORY=Azure/terraform-azurerm-avm-res-<RP>-<modulename>"
./avm grept-apply
$env:GITHUB_REPOSITORY_OWNER="Azure"
$env:GITHUB_REPOSITORY="Azure/terraform-azurerm-avm-res-<RP>-<modulename>"
./avm grept-apply
Custom Variables and Secrets for end to end tests
The respository has an environment called test, it has have approvals and secrets applied to it ready to run end to end tests.
- In the unusual circumstance that you need to use your own tenant and subscription for end to end tests, you can override the secrets by setting
ARM_TENANT_ID_OVERRIDE, ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID_OVERRIDE, and ARM_CLIENT_ID_OVERRIDE secrets. - If you need to supply additional secrets or variables for your end to end tests, you can add them to the
test environment. They must be prefixed with TF_VAR_, otherwise they will be ignored.
4. Review the module
Once the development of the module has been completed, get the module reviewed from the AVM Core team by following the AVM Review of Terraform Modules process here which is a pre-requisite for the next step.
5. Publish the module
Once a module has been reviewed and the PR is merged to main. Follow the below steps to publish the module to the HashiCorp Registry.
Ensure your module is ready for publishing:
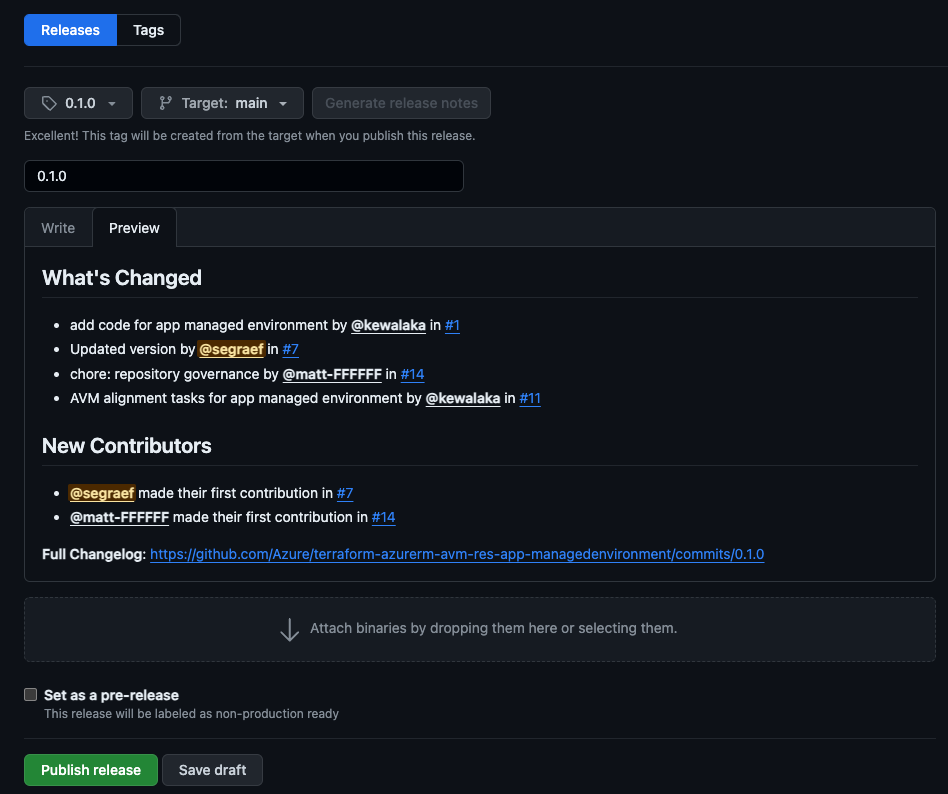
Create a release with a new tag (e.g. 0.1.0) via Github UI.
- Go to the releases tab and click on
Draft a new release. - Ensure that the
Target is set to the main branch. - Select
Choose a tag and type in a new tag, such as 0.1.0 Make sure to create the tag from the main branch. - Generate the release notes using the
Generate release notes button. - If this is a community contribution be sure to update the ‘Release Notes` to provide appropriate credit to the contributors.

Elevate your respository access using the Open Source Management Portal.
Sign in to the HashiCorp Registry using GitHub.
Publish a module by selecting the Publish button in the top right corner, then Module
Select the repository and accept the terms.
Info
Once a module gets updated and becomes a new version/release it will be automatically published with the latest published release version to the HashiCorp Registry.
Important
When an AVM Module is published to the HashiCorp Registry, it MUST follow the below requirements:
- Resource Module:
terraform-<provider>-avm-res-<rp>-<ARM resource type> as per RMNFR1 - Pattern Module:
terraform-<provider>-avm-ptn-<patternmodulename> as per PMNFR1
This section describes the process for AVM owners who are responsible for creating their Terraform Module repositories.
Important
If this process is not followed exactly, it may result in your repository and any in progress code being permanently deleted. Please ensure you follow the steps exactly as described below.
1. Add yourself to the Module Owners Team and Open Source orgs
If you have already done this, then you don’t need to do it again and can skip this section.
- Open the Open Source Portal and ensure you GitHub account is linked to your Microsoft account
- Open the Open Source Portal and ensure you are a member of the
Azure and Microsoft organizations (you need to be a member of both for this process to work) - Navigate to Core Identity and request access to the
Azure Verified Module Owners Terraform entitlement
Info
Please note that until your request is approved to join the Azure Verified Module Owners Terraform entitlement, you will only be able to contribute to your new repository if you JIT elevate first.
You’ll need to gather the following information from the module request issue and other sources:
- Module name: This will be in the format
avm-<type>-<name>. e.g. avm-res-network-virtualnetwork - Module owner GitHub handle: This is your own GitHub handle
- Module owner display name: This is your name in the format
Firstname Lastname. This is used to display the module owner in the module index CSV file - Module description: The description will automatically be prefixed with
Terraform Azure Verified <module-type> Module for ..., where <module-type> is either Resource, Pattern, or Utility - Resource provider namespace: This is only required for resource modules. You may need to look this up in the Azure Documentation if not included in the issue. For example,
Microsoft.Network for a Virtual Network module - Resource type: This is only required for resource modules. You may need to look this up in the Azure Documentation if not included in the issue. For example,
virtualNetworks for a Virtual Network module - Module alternative names: Consider if it would be useful to search for this module using other names. If so, add them here. This is a comma separated list of names
- Owner secondary GitHub handle: This is optional. If the module has a secondary owner GitHub handle
- Owner secondary display name: This is optional. If the module has a secondary owner, get their display name in the format
Firstname Lastname. This is used to display the module owner in the module index CSV file
3. Create the repository
Check you have the latest version of the Terraform CLI installed. You can do this by running terraform -version in a terminal. If you don’t have it installed, you can download it from the Terraform website.
Check you have the latest version of the Azure CLI installed. You can do this by running az --version in a terminal. If you don’t have it installed, you can download it from the Azure CLI website.
Check you have the latest version of the PowerShell Core installed. You can do this by running pwsh -version in a terminal. If you don’t have it installed, you can download it from the PowerShell website.
Open a PowerShell core terminal
Clone the https://github.com/Azure/avm-terraform-governance repository and navigate to the tf-repo-mgmt folder
cd ~
git clone "https://github.com/Azure/avm-terraform-governance"
cd ./avm-terraform-governance/tf-repo-mgmt
Install the GitHub CLI if you don’t already have it installed: https://cli.github.com
Login to GitHub CLI
gh auth login -h "github.com" -w -p "https" -s "delete_repo" -s "workflow" -s "read:user" -s "user:email"
Follow the prompts to login to your GitHub account.
If you are not already logged in to the Azure CLI, you’ll need to be to avoid an error. You don’t need to be connected to any specific subscription or tenant, just a valid session. If you are not logged in, you can run the following command to login to a non specific session:
az login --scope https://graph.microsoft.com/.default --allow-no-subscriptions
Run the following command, replacing the values with the details you collected in step 2
if(!(Test-Path -Path "./scripts/New-Repository.ps1")) {
Write-Error "This script must be run from the tf-repo-mgmt directoy. Please switch to the tf-repo-mgmt directory and try again."
exit 1
}
# Required Inputs
$moduleProvider = "azurerm" # Only change this if you know why you need to change it (Allowed values: azurerm, azapi, azure)
$moduleName = "<module name>" # Replace with the module name (do not include the "terraform-azurerm" prefix)
$moduleDisplayName = "<module description>" # Replace with a short description of the module
$resourceProviderNamespace = "" # Replace with the resource provider namespace of the module (NOTE: Leave empty for Pattern or Utility Modules)
$resourceType = "" # Replace with the resource type of the module (NOTE: Leave empty for Pattern or Utility Modules)
$ownerPrimaryGitHubHandle = "<github user handle>" # Replace with the GitHub handle of the module owner
$ownerPrimaryDisplayName = "<user display name>" # Replace with the display name of the module owner
# Optional Metadata Inputs
$moduleAlternativeNames = "" # Replace with a comma separated list of alternative names for the module
$ownerSecondaryGitHubHandle = "" # Replace with the GitHub handle of the module owner
$ownerSecondaryDisplayName = "" # Replace with the display name of the module owner
./scripts/New-Repository.ps1 `
-moduleProvider $moduleProvider `
-moduleName $moduleName `
-moduleDisplayName $moduleDisplayName `
-resourceProviderNamespace $resourceProviderNamespace `
-resourceType $resourceType `
-ownerPrimaryGitHubHandle $ownerPrimaryGitHubHandle `
-ownerPrimaryDisplayName $ownerPrimaryDisplayName `
-moduleAlternativeNames $moduleAlternativeNames `
-ownerSecondaryGitHubHandle $ownerSecondaryGitHubHandle `
-ownerSecondaryDisplayName $ownerSecondaryDisplayName
For example:
if(!(Test-Path -Path "./scripts/New-Repository.ps1")) {
Write-Error "This script must be run from the tf-repo-mgmt directoy. Please switch to the tf-repo-mgmt directory and try again."
exit 1
}
# Required Inputs
$moduleProvider = "azurerm" # Only change this if you know why you need to change it (Allowed values: azurerm, azapi, azure)
$moduleName = "avm-res-network-virtualnetwork" # Replace with the module name (do not include the "terraform-azurerm" prefix)
$moduleDisplayName = "Virtual Networks" # Replace with a short description of the module
$resourceProviderNamespace = "Microsoft.Network" # Replace with the resource provider namespace of the module (NOTE: Leave empty for Pattern or Utility Modules)
$resourceType = "virtualNetworks" # Replace with the resource type of the module (NOTE: Leave empty for Pattern or Utility Modules)
$ownerPrimaryGitHubHandle = "jaredfholgate" # Replace with the GitHub handle of the module owner
$ownerPrimaryDisplayName = "Jared Holgate" # Replace with the display name of the module owner
# Optional Metadata Inputs
$moduleAlternativeNames = "VNet" # Replace with a comma separated list of alternative names for the module
$ownerSecondaryGitHubHandle = "" # Replace with the GitHub handle of the module owner
$ownerSecondaryDisplayName = "" # Replace with the display name of the module owner
./scripts/New-Repository.ps1 `
-moduleProvider $moduleProvider `
-moduleName $moduleName `
-moduleDisplayName $moduleDisplayName `
-resourceProviderNamespace $resourceProviderNamespace `
-resourceType $resourceType `
-ownerPrimaryGitHubHandle $ownerPrimaryGitHubHandle `
-ownerPrimaryDisplayName $ownerPrimaryDisplayName `
-moduleAlternativeNames $moduleAlternativeNames `
-ownerSecondaryGitHubHandle $ownerSecondaryGitHubHandle `
-ownerSecondaryDisplayName $ownerSecondaryDisplayName
The script will stop and prompt you to fill out the Microsoft Open Source details.
Open the Open Source Portal using the link in the script output.
If you see the Complete Setup link, then follow the steps below in 3.1. If you don’t see the Complete Setup link, then follow the steps in 3.2.
3.1 Complete Setup Link is Present
Click Complete Setup, then use the following table to provide the settings:
| Question | Answer |
|---|
| Classify the repository | Production |
| Assign a Service tree or Opt-out | Azure Verified Modules / AVM |
| Direct owners | Add yourself and jaredholgate or mawhi as the direct owners. Add the avm-team-module-owners as the fallback security group. |
| Is this going to ship as a public open source licensed project | Yes, creating an open source licensed project |
| What type of open source will this be | Sample code |
| What license will you be releasing with | MIT |
| Did your team write all the code and create all of the assets you are releasing? | Yes, all created by my team |
| Does this project send any data or telemetry back to Microsoft? | Yes, telemetry |
| Does this project implement cryptography | No |
| Project name | Azure Verified Module (Terraform) for ‘module name’ |
| Project version | 1 |
| Project description | Azure Verified Module (Terraform) for ‘module name’. Part of AVM project - https://aka.ms/avm |
| Business goals | Create IaC module that will accelerate deployment on Azure using Microsoft best practice. |
| Will this be used in a Microsoft product or service? | This is open source project and can be leveraged in Microsoft service and product. |
| Adopt security best practice? | Yes, use just-in-time elevation |
| Maintainer permissions | Leave empty |
| Write permissions | Leave empty |
| Repository template | Uncheck |
| Add .gitignore | Uncheck |
Click Finish setup + start business review to complete the setup
Wait for it to process and then click View repository
If you don’t see the Elevate your access button, then refresh the browser window
Click Elevate your access and follow the prompts to elevate your access
3.2 Complete Setup Link is Not Present
Click on the Compliance tab
Fill out the 3 sections as follows, saving each:
| Question | Answer |
|---|
| Direct owners | Add yourself and jaredholgate or mawhi as the direct owners. Add the avm-team-module-owners as the fallback security group. |
| Classify the repository | Production |
| Assign a Service tree | Azure Verified Modules / AVM |
Head back to the Overview tab
If you don’t see the Elevate your access button, this is likely because you already have temporary admin rights from creating the repository. In that case you’ll see You currently have native Administrator permission to this repository on GitHub. and you can skip the next step
If you do see the Elevate your access button, click it and follow the prompts to elevate your access
Now head back over to the terminal and type yes and hit enter to complete the repository configuration
Open the new repository in GitHub.com and verify it all looks good.
The script will automatically create a pull request to add the module metadata to the avm-terraform-governance repository. This will be approved and merged by the core team. You can find it here if you lost the link.
The script will automatically create an issue to install the Azure Verified Modules GitHub App in the repository. This will be actioned by the open source team. You can find it here if you lost the link.
4. Update the Issue Status
- Add the Status: Repository Created 📄 label to the issue
- Remove the Status: Ready For Repository Creation 📝 label from the issue if it was added
5. Wait for the GitHub App to be installed
Once the GitHub App has been installed via the issue raised by the script, the sync to create the environment and credentials will be triggered automatically at 15:30 UTC on week days. This will complete the repository creation process.
The open source team will usually complete this within 24 hours, but it can take longer in some cases.


